INTRODUCTION
Motivation is one of the important parts of managerial functions. A manager becomes unsuccessful if he fails to motivate his subordinates. The motivated workers perform their duties with full responsibility.
The development of self-responsibility among the workers contributes for the best utilization of available resources like materials, money, machines & others. At the first chapter the student has mentioned what is motivation, the factors affecting motivation & both content & process theories were critically evaluated by comparing their own weaknesses along with the strengths. The second chapter demonstrated that a brief introduction about Halanka & at the latter part of the chapter, the strategies of Halanka & strengths & weaknesses have explained in detail. And finally at the third chapter, the student suggests some recommendation which have sharpened by the enamours literature which should use by Halanka to motivate their employees to attain the desired out comes successfully.
CHAPTER ONE
INTRODUCTION
1.0. Introduction
This is the chapter that expects to provide a basic idea about the entire study. The first section is going to discuss about the definitions of motivation, the different theories of the motivation & factors which affecting to the motivation. Lastly it discussed the sequence of arranging the study along with various topics.
1.1. The Concept of Motivation
“Don’t be pushed by your problems; be led by your dreams” (Unknown)
No matter who you are, everyone is striving to motivate someone. Parents try to motivate their children to study. Bosses try to motivate their employees to work faster. People try to motivate themselves to lose weight. How to motivate myself to keep going even when things get hard. How to motivate vendors to work with the organizations. Motivation is an external force that requires either a threat or a reward. But once that carrot or stick is removed, everything falls apart.
There are infinite number of definitions which to refine the word of motivation have emerged throughout the world over the time. Some selected definitions of the motivation have illustrated by the table 1.1.
Table.1.1. Different Definition of the Motivation
| Author/ Article/Web Site | Definition |
| Oxford Dictionary | Provide (someone) with a reason for doing something |
| Wikipedia | Motivation is the reason for people’s actions, desires & need. Motivation is also one’s direction to behaviour what causes a person to want to repeat a behaviour. A motive is what prompts the person to act in a certain way or at least develop an inclination for specific behaviour. |
| The Book of “Management by Richard L Daft” | Motivation refers to the forces either within or external to a person that arouse enthusiasm and persistence to pursue a certain course of action. Employee motivation affects productivity, and part of a manager’s job is to channel motivation toward the accomplishment of organizational goals. |
| Student | Motivation is the inner state that causes an individual to behave in a way that ensures the accomplishment of some goal. In other word, motivation explains why people act as they do. |
Source: Developed by the Student
1.2. The History of Motivation
Many researchers had assumed that human behaviour is guided by the desire to feel good which is known as “Pleasure Principle”. (Historical Perspective on Motivation). The way of originating “Motivation” to the world is shown by table 1.2.
Table.1.2. Evolution of Motivation
| Period | Author | Step of the Evolution |
| 427 B.C.-347 B.C. | Plato |
|
| 1842-1910 | William James |
|
| 1856-1939 | Sigman Fraud |
|
| 1870-1937 | Alfred Adler |
|
| 1871-1938 | William McDougall |
Ex: Savings, Construction, Curiosity & etc |
| 1875-1961 | Carl Jung |
|
| 1884-1967 | Clark Hull & Kenneth Spence |
Ex: Drive to eat when hungry…. |
| 1893-1988 | A.Murray |
|
| 1902-1994 | Erik Erikson |
|
| 1902-1987 | Cal Rogers |
|
| 1904-1990 | B.F.Skinner |
|
Source: Developed by the Student by using the article of Historical Perspective on Motivation.
It is not the time to discuss all the footsteps of the evolution of motivation. Therefore, some remarkable benchmarks of the history just only explored by table 1.2.
1.3. Motivation in Buddhism
“Be strong but not rude, be kind but not weak, be humble but not shy, be proud but not arrogant” (Buddha)
The trend of the business world is spending lots of time & money to motivate the employees to achieve the organizational desired out comes. But, Robin Beck has declared that Buddhism offers an effective & self-directed practice to change motivation for the better. Due to the Buddhist teaching for motivation cannot be categorized or compared with modern or classic motivational theories. Anyway as a teacher Buddha mentioned about his damma as “hi passak” which means “come & see” that focuses on self-motivation. In the most of times, the Buddha explains about self-motivation is only way to get rid of that samsara. When examining the Thripitaka that gives lots of Damma preached about motivation like below,
- Kalama Sutta
This mentions about self-motivation as Kalamas, as you yourselves say, do not follow the leader, do not go by the examinations of reasons, do not stick to wrong views & etc. Kalamas, you know yourself, these thoughts are demerit, faulty, blame by the wise, undertaken & accomplish are not for welfare. They conduce to please, then you should grow them. (Thikaniapata)
- Mahamangala Sutta
Mention eleven factors which are possible that the bhikku could come to growth & increase in this Teaching & Dispension Bhukkus,
As a conclusion Buddhist teaching for motivation basically mean self-motivation. It is helpful to the people to fulfil their aims & goals certain. “Atti attano nto- kohi nto parosiy”, hoping someone’s help is useless. Because of that we can get only help from our self. If someone can think like that he absolutely provides his full capability to attain the goals without any barriers.
1.4. Importance of Motivation
There are several factors which make the motivation of the employees is highly significant to an organization.
- Increased Productivity
- Improved Employee Morale
- More Loyal Workforce
- Better Creativity
- Appraisal Opportunities
(Importance of Employee Motivation, n.d.)
1.5. Factors Affecting to the Motivation
Brain Tracy has declared that, there are four factors exist in every organization to determine the level of motivation in his article of “The Four Factors of Motivation”. They are,
- Leadership Style
This is the key factor in determining how people feel about the company & how motivate they are. The appropriate leadership styles depend on the goal & objectives of the organization. Sometimes, the managers have required to use different leadership styles for different kind of people under differing circumstances.
- The Reward System
Each & every organization has a specific type of reward structure often differing from person to person & from department to department. There is a saying that, “If you want more of something in an organization, simply increases greater rewards for that behaviour, if you want less of an activity in an organization, simply reduce the rewards or increase the punishment or disproval for that behaviour. People respond to incentives. (LeBoeuf)
- The Organizational Climate
The climate of the organization deliberately creates & maintains by the management. It largely consists of the way that people treat each other up & down the line.
- The Structure of the Organization
Some works are inherently motivational, requiring creativity, imagination & high level of energy. Work that involves communicating, negotiating & interacting with other people in order to gain their cooperation to get the job done quickly & well brings out the best energies of the individual. It is exciting & challenging & also usually high rewarding. In other hand, large number of work must be standardized, routinized, & made relatively unexciting in order to be done efficiently & cost effectively. It is hard to motivate factory workers who work on a production line all day & whose activities are carefully monitored & regulated to ensure maximum level of productivity.
Ralph Heibutzki introduce any other factors which effect on motivation in the article of “What are the factors affecting motivation in an organization?”. They are,
- Autonomy
Employees are more desire to feel engaged if they find their work meaningful & have the freedom to make choices in how it’s done.
- Financial
Bonuses & incentives play an important role in keeping employees motivated, but usually work best as part of a comprehensive program that provides opportunities grow.
- Flexibility
Condensed work schedules, flexible workweeks & telecommuting have become popular options for employee looking to balance their professional & personal lives.
- Recognition
Although the chance to earn higher pay is important, employees also want to feel their employer cares about them personally. That’s why any reward program must provide opportunities to recognize individual effort.
1.6. Motivational Theories
Several theories have developed over the time. Mainly they can classify into below way,
Figure.1.1. Motivational Theories
Source: Developed by the Student
All the sub theories critically analysis by table.1.3 rather than just defining them,
Table.1.3. Different Motivational Theories
| Theory | Definition | Importance | Limitations | |
| Maslow’s’ Hierarchy of Needs | There are five independent level of basic human needs which must be satisfied strict sequence starting with the lowest level. |
|
| |
| ERG Theory of Alderfer | Consists three group of core needs; existence, relatedness & growth; that a person has & seek to fulfil them |
|
| |
| Gregor’s Theory X & Theory Y | Describes a contrasting models of workforce motivation applied by the managers in HRM, OB, OC &OD |
|
| |
| Employees’ job satisfaction is influenced by both hygine & motivator factors |
|
| |
| McClelland’s Theory of Needs | Explains that, how the needs for achievement, power & affiliation affect the actions of people from a managerial context. |
|
| |
| Cognitive Evaluation Theory | Explains the effects of external consequences on internal motivation |
|
| |
| Goal Setting Theory | Refers to the effects of setting goals on subsequent performance. |
|
| |
| Self-Efficacy Theory | The beliefs become a primary explicit explanation of motivation |
|
| |
| Reinforcement Theory | Refers that, some one’s behaviour can change by using reinforcement, punishment & extinction. |
|
| |
| Equity Theory | Based on the idea that individuals are motivated by fairness & if they identify inequities in the input or output ratios of themselves & their referent group they will seek to adjust their input to reach their perceived equity. |
|
| |
| Vroom’s Expectancy Theory | Assumes that behaviour results from conscious choices among alternatives whose purpose it is to maximise pleasure & to minimize pain. |
|
| |
Source: Developed by the Student by basing on Several Literature
CHAPTER TWO
HaLANKA GROUP
2.0. Introduction
Very firstly this chapter gives a brief introduction about the selected organization which the student is currently working. Secondly, it broadly discusses the motivational strategies that use by the organization. After that, the strengths & weaknesses are going to explore by comparing with the reputed market leaders’ motivational strategies.
2.1. Introduction about Halanka Group
In here, the student has discussed about the organization by dividing chapter into several parts such as history, product category, workforce & etc.
2.1.1. History of the Organization
In 1988, the group of Helanka has commenced in Ehaliyagoda by the cooperation of two siblings who named as Mr.Rehena de Silva & Mr.Kapila de Silva. They are able to maintain a profitable relationship with more than 20,000 loyalty customer base by utilizing their 30 years’ industry expertise while possessing Rs.500mn annual revenue. Currently both of owners have maintained separate ownership of six showrooms. From among them, Mr.Kapila serves as the Managing Director by taking the ownership of the largest footwear showroom in Sri Lanaka which locates in Negambo while other two entities are operating in Horana&Awissawella .
2.1.2. Vision of the Organization
“To be the most preferred & admired retailer in the industry while being socially responsible”
2.1.3. Mission of the Organization
To setting up a remarkable chain of shoe shopping malls where customer satisfactions are met beyond their expectations”
2.1.4. Product Classification of the Organization
Halanka is a leading footwear retailer in the areas of Awissawella, Ehaliyagoda, Negambo, Horana, Piliyandala with a comfortable, durable & fashionable shoes. It is not just like a common footwear retailer which means they strive to fulfil the shoe requirement of the customers more than their expected level. Anyone can easily understand that uniqueness of Halanka by only entering into one of showroom. The mass product range classification is depicted by 2.1. figure like below,
Figure.2.1. The Production Classification of the Organization
Source: Developed by the Student
Figure.2.1.1. The Footwear Classification
2.2. The Motivational Strategies of the Organization
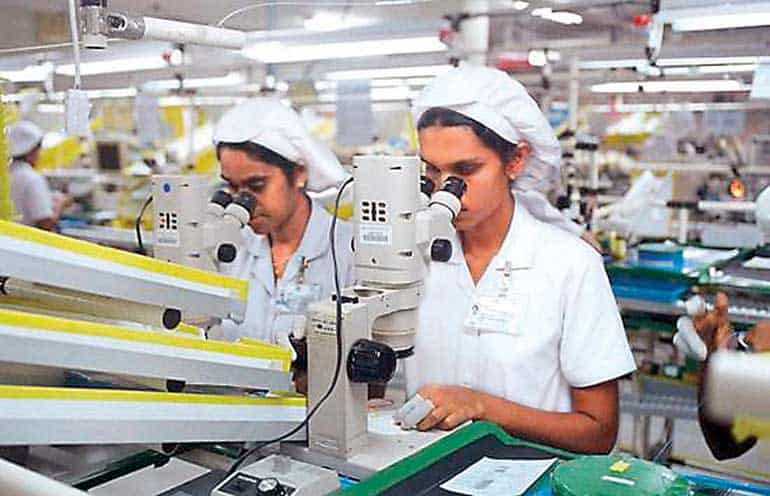
The entire workforce of the organization is only 98 including both managerial & non-managerial level employees. From among them, more than 60% of the employees are related with direct front line sales people. Therefore, each & every motivational programmes are conducted by giving higher priority to those people. Because Halanka believes that, they are the service people who directly engage with the customers by back up through other employees. Below mentioned factors & strategies have implemented to energize the employees of the organization to achieve the desired out comes of the entity.
2.2.1. Monetary Reward
The wage or salary paid is an instrument of motivation or driver for the workforce to keep the body & soul together & possibly make them a stakeholder in the organization. (Agburu, 2012)
Halanka is still a growing company just only have 6 showrooms in six areas. Even the branches are limited they have already acquired the leadership of the market by giving a sharp competition to other reputed shoe brands in Sri Lanka such as Bata, DSI & etc. When comparing to other small shoe retailers in the local areas, Halanka has given a remarkable salary to the employees. That’s why more than 30% of the workforce has more than 2 year working experience. The way giving monetary reward is clearly explored by table 2.1.
Table.2.1. Monetary Rewards of Halanka
| Salary above the market level | Competitive basic salary than other competitors. Average salary of Halanka employee is relatively more than 15% percent than other competitors. |
| Performance Allowance | Considerable level of allowance has added to the basic salary based on the service period. This allowance is paid for the achievement of KPI. |
| Attendance Allowance | Both managerial & non managerial employees are entitled to receive an allowance for their attendance. |
| Incentive & Bonus | Whenever there is a promotion, after ending that, the net profit of the promotion is distributed to all the employees due to a proportion. Ex: Rasi wasi, Kuttam Wattam |
| Loyalty Card Allowance | This is eligible only for the sales people who achieve the target loyalty card selling, he is rewarded by a money allowance in relevant to the related month. |
| Special Allowance | This is also related to the sales people who sell the non-moving item he can take this money allowance additionally to his monthly salary. |
Source: Developed by the Student
2.2.2. Non-Monetary Reward
The need for recognition, self-respect, growth, meaning full work, social activities are as important as monetary incentives in increasing the employees’ morale & motivation. (Nilay, 2004)
As a private sector organization, Halanka also has a growing interest & attention on the use of non-monetary incentives to enhance the productivity of the employees. The currently use, non-cash rewards are illustrated by table 2.2.
Table.2.2. Non-Monetary Rewards of Halanka
| Insurance Benefit (The company incurs Rs.1200 & Rs.850 per employee monthly for the both insurance respectively while the employees don’t need spent even one cent for this insurance coverage) |
|
| Gifts |
|
| Uniform |
|
| 15% Discount |
|
| Awarding Ceremony |
|
Source: Developed by the Student by basing on the Discussion had with the Human Resource Executive at Halanka.
2.3. Strengths & Weakness of the Motivational Strategies of the Organization
The strengths & the weaknesses of the motivational strategies of Halanka are discussed in detail by the table.2.3.
Table.2.3. Strengths & Weaknesses of the Motivational Strategies of Halanka
| Type of the Reward | Strategy | Strengths | Weaknesses |
| Monetary Reward |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
| Non-Monetary Reward |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Ex: In last year, the best manager was awarded by a holiday at a resort. But actually he didn’t require that because natively he doesn’t like to stay in resorts. Therefore, finally the management had to give the money which has reserved for him as a cheque. |
Source: Developed by the Student
The commonly use motivational strategies of Halanka Group have discussed in detail by previously mention tables. But there are some weaknesses which can be seen throughout the entire group that directly influence to demotivate the employees. They are,
- All the employees are not eligible to use mobile phones at the working period. Especially sales people. At the morning, the manager collects all the personal phones into a luggage & the phones give back to them after closing the showroom. Approximately it may at 9.00 p.m. If there is a special reason the families of the employee can call to the office phone. Even for the head office people can only use mobile phones at the lunch & tea time. In last year, one of front line officer who has worked more than 3 years with the company, had to leave the Halanka after his marriage because of this reason.
- All the motivational programmes conduct on the basis of considering all the employees are equal. The management considers all the employees can be motivated & energised by using same tool. But it is not the true, the world accepted motivational rule is, several employees are motivated by multiple factors. In here also, the workforce is made by a mix of variety nature people. All of them are completely differed due to their education, age, sex, experience & etc. And also, all the motivational strategies are extrinsic. There is no any strategy to pop up the intrinsic value of the employees.
CHAPTER THREE
CONCLUSION & RECOMMENDATION
3.0. Introduction
This is the chapter which finally goes to provide recommendation after concluding all the facts of the report. The first section declares the potential solutions which can be used by Halanka at the future to motivate its employees while the latter part presents a summarize about the entire study.
3.1. Recommendation
In here, the student provides recommendation which can be used by the management of Halanka to boost the energy of the employee to achieve the desired organizational out comes by reducing the weakness of the existing strategies. They are,
- If the monetary reward is to be motivating it must satisfy a minimum of three conditions like,
- It has to be felt by the employee:
It must be in such amount or form so that an employee feels appreciated for their effort. If this condition is not met, the received reward will not be valuable for the employee. They will regret the efforts incurred to obtain it. While the reward will pose demotivating impact on the employee instead of motivating.
- The reward should not be excessively delayed in time
It should be granted as soon as possible after the fulfilment of the conditions determining its receipt. Otherwise, if the time is inaccurate, the employee can forget the reason of being awarded the allowances, the positive behaviour & attitude will be lost.
- The reward in its essence cannot be granted to all
If each employee receives it in the same amount, regardless of their personal contribution to the realization of the task, the reward does not meet its motivational function. (Vroom, 1966)
- Empowerment refers to the employee’s feeling of being effective, in control & influential. It improves employee commitment, creativity, productivity, satisfaction & motivation. Effective motivation comes from within the individual. Empowerment is a factor that enables better performance through appreciation, meaningful work, a happy & flexible work environment & feeling of personal achievement. And also, the empowerment should run with the training, coaching & creation a collaborate in good faith for the company to have consistent good performance. The management need to listen to employees & addresses their concerns for the work environment to be genuinely collaborative. (Sarkissian, 2017)
- Rits Carlton who is the giant of hotel industry over the world, has given full authority to the front level officers to take any decisions whenever they need to solve a customer problem.
- The management can find creative ways in which to consistently keep their employees motivated as much as possible.
Ex: Post a positive quote or picture by the copier, coffee machine or somewhere else that is visible & that receives high foot traffic so that others can see.
- Employees also want to see the company that they are working for succeed. Many have excellent ideas, ranging from money saving to operational improvements. So the management must take an effort to take some time to ask & listen to suggestions. Nothing is more worthwhile than feeling valued.
- According to the preaches of Buddhism, self-motivation is the best way to enhance the job satisfaction of the employees. Then Halanka can use below strategies to enrich the self-motivation of the employees.
Ex: Encourage the employees through their mistakes
Refer the employee to attitude development programme
Arranging stress decrease programme like yoga, sports, healthy food & etc.
3.2. Conclusion
The ultimate corollary of the study is developed by using all the facts which have discussed in this report previously. The employees are the most valuable assets & managing them is critical. This is especially true for small businesses where employee productivity is a serious concern. However, the management can’t blame the employees alone for lower productivity. Employers too play a significant role in motivating their workforce to become more productive at work. After all employee satisfaction plays key role in boosting productivity & can finally impact the company’s bottom line. Halanka is a growing shoe retailer in Sri Lanka by utilizing a valuable human resources. The easiest way of increasing motivation is “Communication” by having positive communication at the workplace. Not relying only on emails but by making sure they talk to their employees in person & even on a personal level. And also, the management should ensure their employee on how their individual efforts & contribution plays an important part of the company’s overall goals & directions. The management must make sure that to feel to the employees that their work & effort is an important contribution to the company’s success. Remember to always keep an “Open Door Policy” & have an approachable management team.
Bibliography
Agburu, J. (2012). Recent Trends in Wage & Salary Administration in Nigeria. International Journal of Basic & Applied Science, 257-268.
Buddha, L. (n.d.).
Historical Perspective on Motivation. (n.d.).
Importance of Employee Motivation. (n.d.). Retrieved from speedupcareer.com.
LeBoeuf, M. (n.d.). The Greatest Management Principle in the World”.
Nilay, Y. (2004). The Use of Non-Monetray Incentives as a Motivational Tool: A Survey Study in Public Organization in Turkey. Turkey.
Sarkissian, A. (2017). How Does Empowerment Affect an Employee’s Motivation & Performance. Retrieved from Chron: smallbusiness.chron.com
Thikaniapata. (n.d.). 3.2.2.5 Anguttara Nikaya.
Unknown. (n.d.).
Vroom, V. (1966). Work & Motivation. Wiley.



4 comments