Introduction
The organizations have to develop their strategies in such ways that they will meet the expectations of the customers; if the customer requirements are not appropriately met, the organizations eventually fail to achieve the results they seek (Ole Friis, 2016). The operations of the organization will have to be developed in line with the expectations of the customers. The customers have a value set that they expect to be fulfilled and having the right kind of value approach will allow them to achieve these targets. Thus, the benefits affiliated with these areas are important to reach the future targets that are in place.
The organization that is in consideration is ABC Retailer Chain; this is the largest of the supermarket chains in Sri Lanka. the company has around 315 supermarket outlets currently. They have the ability to access the products from the appropriate suppliers and due to the outlet strength, that they have, they command the supply chain effectively too.
In order to evaluate the key aims, the mission and the vision of the company has to be identified (Veit Etzold, 2008). The mission and the vision in this regard indicate as to the reason that the company is in operations.
2.0 Key aims of the organization
Vision – To be a global corporate role model in community – friendly national development.
Mission – Serve the rural community, our customers and all other stakeholders, through our core business – food with love – and other related businesses, based on the three main principles of;
- reducing the cost of living
- enhancing youth skills
- bridging regional disparity
by enhancing local and global markets.
The main targets of the company for the future can be highlighted as follows:
- The company has seen the number of outlets increase of 315 outlets in 2017 compared with 297 in 2016. The company expects this to grow to reach 225 by end of 2018.
- The company has seen the revenue reaching Rs.84 billion in 2017, an annual increase of 20%; the top line growth is expected to be around 10% continuously for the next five-year period.
- The company has seen the net margin grew to 2.7% in 2017 compared with 2.4% in 2016; this is expected to grow to reach 3.5% in next year.
- The company has not revealed the average sales to floor area; however, the company is expecting to see a continuous increase of 7.5% on average for this over the next five years.
3.0 Competitors
It is important to note that the modern trade penetration levels in Sri Lanka is very low; around 15% (Cargill’s, 2018). This indicates that the supermarket field of the country has much room to grow. However, the current supermarket concentration is primarily around Western province of the country and the main concentration point is the Colombo City and the suburbs. Two of the main competitors can be compared with company’s retailing operation. Laugfs, the smallest in the market has not revealed segment details for the supermarket they operate.
| ABC | Keels | Arpico | |
| Outlets | 315 | 64 | 61 |
| Segment revenue | 66,345 | 29,814 | 24,754 |
| Segment growth | 19.6% | 32.1% | 12.9% |
| Capex as a % of revenue | 2.5% | 5.9% | 2.5% |
Table 1 – Comparison of the competitors (FitchRatings, 2018)
ABC claim that they hold above 51% of the market share; this indicates that they have a commanding position in the market and when compared with the other supermarkets, the company plays a commanding ole in the market. Thus, the role of the company in this competitive market place is an important one. While the company is placed in a relatively comfortable position in this market, it is also important to note that the company has to face growing competition from Keels as well as Arpico. These companies also have the ability as well as the resources to develop their supermarket segment and continue to grow in the future. Keels has a very high capital investment and this indicates that they are continuously modernizing the supermarket outlets that they have and the result eventually is that the ABC might have to look to these developments in the future as a challenge for them.
4.0 Target customers
The main set of target customers in this instance involve that those who seek to purchase high quality and fresh products. The company has developed the required supply chain relationships with the op suppliers and this ensures that they will be able to provide the markets with the high-quality products in line with the expectations they have (Rainer Feurer, 1995).
Figure 2 – Target customer group
It can be seen as shown above that the main target market is those who seek for a quality product and they want the predict at a reasonable price point. This indicates that ABC have to provide quality products to the market and meet the specific outcomes that they have identified to be in place. The company is seeking to become the lowest cost provider of the items. The supermarket is competing with the other alternatives such as the regular groceries with the prices and make sure that they stay ahead of the competition in the market.
5.0 Order qualifying and winning
The order qualifying factor is to offer the customers with the brands they need at the suitable price points. The supermarket has been able to provide the customers with the specific brands they need (Marx, 2015). Also, these brands are offered to the customers at an appropriate price point. Thus, the company has been able to balance the order qualifying aspects and adhere to the requirements of the supermarket industry overall. Having the ability to quality would allow them to meet the market expectations and make sure the required results are catered to (Grazzini, 2013).
However, the price is the main order winner for the company. ABC have been able to always offer the customers with the lowest of the market prices. This in other words highlights the fact that the customers will be able to purchase the products they need at the lowest possible prices that they seek to purchase these products. Thus, the price of the products drives the customers to make the purchase decision in line with the expectations that they have with the products that are available with ABC outlets.
6.0 Supply chain
The supply chain indicates as to how the products and the services have been distributed. As the company is a supermarket, there are many types of supply chains integrated with the supermarkets. There are instances that the company purchases directly from the original manufacturers. For instance, the case of vegetables, the retailer chain directly purchases from the farmers. On the other hand, there are some other products which are reaching other company through the suppliers. For instance, certain international brands are purchased by the agents locally and they would provide these products to the company.
7.0 Operations management concepts
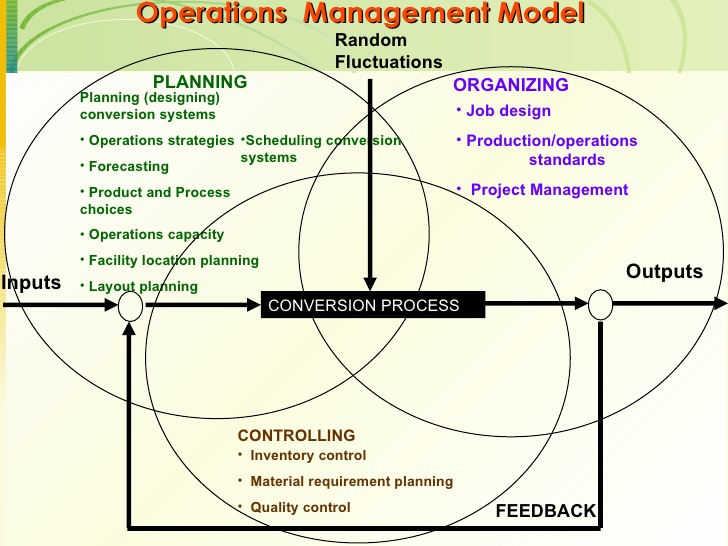
ABC have to ensure they provide the customers with the service matching the specifications they are in need of. The following model highlights as to the main operating model that the company has in place and how they use these to provide the specific results in need.
Figure 3 – Operating model
Quality – This is very important and the company has to work with the suppliers to ensure they deliver the required quality. There are specific quality measures and the suppliers will need to ensure these quality aspects are ensured.
Plan – The company observe the capabilities of the suppliers and plan with them in ensuring they supply the needed products in needed quantities.
Organizing- ABC will check the products before placing them in the stores. Thy will also make sure that they carry out random quality checks to ensure the quality is preserved at the stores. The needed storage condition is also maintained.
Controlling – If there are quality issues in terms of customer complaints, they will use these to discuss the problem with the suppliers and then make sure that they solve this issue effectively.
Cost – This is the order winner; ABC have to pay extra attention in management of this area.
Plan – ABC will plan to optimize the costs. They will work with the suppliers to plan to minimize the logistics costs. Where the company hand les logistics, they work to reduce any wastage levels.
Organize – The products will be provided to the customers at the intended prices. The target price will have to make sure that an appropriate margin is maintained. The sector is operating with thin margins and this is an issue the company is seeking to overcome in this area.
Control – The company has to maintain logistical planning, employee efficiencies and the required skills maximized to ensure they reduce the cists are improve the benefits affiliate with these areas.
Speed – The company could face stock out situation if they do not have the required level of speed in place.
Plan – Suppliers, logistical planning and the customers are some of the key areas that has to be looked into when the parties manage these areas well. the lead times have to be planned for each of the products and the delivery should be within the plan.
Organize – Products will have to be delivered within the planned time. this is done through managing of the activities and achieving of the needed results. The targets should be achieved by utilizing of resources available.
Control – The delivery standards should be adhered to and the company needs to measure the delivery capabilities to be achieved in time. the right kind of approaches has to be sued therefor.
Dependability – the services have to b dependable; in this instance, the customers have to ensure they have the products they seek for. Having the dependability in place will provide positive outcomes.
Plan – The continuous supply capabilities are evaluated with the suppliers. There are alternative suppliers where available. This plan will ensure the products will be available to the customers when needed.
Organize – The suppliers will deliver the products in time as needed. The IT systems are developed to maintain the stock transparency with the suppliers. So, the supplier can take initiatives to deliver the supplies as required.
Control – The performance of the suppliers is evaluated and the deliver and the delivery times are also evaluated. This will make sure the products are provided to meet the specific customer needs.
Flexibility – ABC have to develop the flexibility to they can manage the internal operations well.
Plan – Each outlet plan for the stocks of the items they need as well as the staff and the other resources requirements. They are generally available at each outlet. In case they are not available, they can raise requests so the other outlets can share some resources.
Organize – There are formal channels where the assistance could be required, the resources could be obtained etc. This will ensure all the outlets operate with the needed resources to maintain quality.
Control – Outlets will need to ensure they are contained with the resources they need. However, the company has to flexibility as they maintain extra resources to meet sudden changes in the resources.
7.0 Conclusion and recommendations
ABC have been able to develop their operations in such a way that they maintain costs under control. The following recommendations will provide more beneficial results.
- The company has to develop a system that will allow them to be integrated with the suppliers; the suppliers should know the stock movement details and replenishments needed. Thus, without placing orders the suppliers could get ready to replenish stocks.
- ABC have to measure the performance of all the services providers to evaluate if they provide their services in time to meet the expectations in terms of the results. Thus, this is another benefit they could achieve.
- The company has to plan each activity so they can reduce the costs. Then they will b able to pass on part of the cost benefit to the customers. This will improve the lower price focus the company has.
References
FitchRatings. (2018). Spotlight: Sri Lankan Modern Grocery Retai. Retrieved from https://lmd.lk/wp-content/uploads/2017/11/Spotlight-Sri-Lankas-modern-grocery-retail-Nov-2017.pdf
Grazzini, F. (2013). How do managers make sense of strategy? European Business Review,, Vol. 25 Issue: 6, pp.484-517.
Marx, T. G. (2015). The impact of business strategy on leadership. Journal of Strategy and Management, Vol. 8 Issue: 2, pp.110-126.
Ole Friis, J. H. (2016). A strategy model – better performance through improved strategy work. Journal of Modelling in Management, Vol. 11 Issue: 3, pp.742-762.
Rainer Feurer, K. C. (1995). Dynamic strategy ownership. Management Decision, Vol. 33 Issue: 4, pp.12-21.
Veit Etzold, T. B. (2008). Metaphors in strategy. Business Strategy Series, Vol. 9 Issue: 5, pp.279-284.


One comment