Chapter 1 – Introduction
1.1 Introduction
A firm is required to maintain customer satisfaction by meeting the needs of the client comprehensively. This is an essential area that needs to be addressed, to ensure one remains competitive (Sabir et al, 2014). The organization will initially require to understand the needs of the customer and subsequently, frame a strategy which will enable them work with the customer, and provide the required outcomes.
The customer satisfaction levels and staying ahead of the competition are two areas which are interlinked; when the customers are satisfied with the services they receive, it is likely that they will continue to transact with the company and patronize the products and services they offer. Therefore, customers will continue to be loyal and stay with such companies and achieve appropriate results in the future (Vukmir, 2006).
The customers can select the bank which suits their needs to the optimum. This is the challenge the banks are faced with. The banks need to provide the exact needs of the customers to ensure that the latter maintain their relationship, continuously. Meanwhile, customers do not need to incur any cost, when changing their preference for the services of a bank. This is an area that banks require to focus (Asher, 1989). Moreover, customers can also maintain accounts with more than one bank since the outcomes will be beneficial to them, as it will lead them to reach appropriate results in the future.
Likewise, to ensure customer retention, banks should consider developing a competitive advantage, which is a critical aspect considered by other businesses. This will give customers a reason to remain with a particular bank, instead of considering another option.
Meanwhile, the bankers have the duty of retaining the customers as this is a competitive business area unlike many other business areas (Amoah-Mensah, 2010). The main challenge is to build this unique domain and assure the customers who require such services that their needs will be fulfilled on a continuous basis, which will enable the bank to benefit from the outcomes in the future.
When the bankers decide how they require to build the competitive advantage and increase customer satisfaction, they also need to evaluate how they can develop products to meet the regulatory requirements. There are several regulations associated with the industry and the parties will have to ensure that they develop their products and services to meet precise market requirements (Munari, Ielasi and Bajetta, 2013). Thus, this remains an important area which the bank needs to address when taking measures to introduce services to the market.
This is the backdrop to the discussion affiliated with the banking industry of Sri Lanka which requires to be undertaken. The banks require to operate in a market where most of the resources are held by the giant state banks. Resultantly, this places additional pressure on the private sector banks to reach positive results in the future, through the appropriate management of wealth and the customer base they possess.
1.2 Research problem
The banking sector of Sri Lanka is one of the most competitive business sectors in operation; since there are in excess 25 Business banks that are currently operating in this space. Further, it is also evident that there are several non-banking financial companies that compete with the banks in this space as well (Central Bank, 2017). The main issue being that the two state commercial banks namely; People’s bank and Bank of Ceylon command over 45% of the asset stake in commercial banking, and recognized as the two largest parties operating in this market space. Subsequently, this leaves the private banks to compete in a highly competitive environment (Work in Sri Lanka, 2017).
Maintaining Customer satisfaction remains a vital area in the banking sector, as it is a critical factor for the banks to achieve, to ensure they fulfil the desired results. Not only do the banks require to meet the needs of the customers in the short to medium term, but they also need to device strategies to retain the customers consistently with the fulfillment of their needs (Bena, 2010). At the same time Banks will have to work towards achieving the expected goals in the future. Thus, the banks will need to ensure that the parties will achieve the results and maximize the benefits associated with these outcomes (Murugiah and Akgam, 2015).
All Sri Lankan banks are regulated by the Central bank of Sri Lanka (CBSL) and there are stringent criteria that the banks are expected to meet. Therefore, it is very difficult for the new players to enter the market due to these rigorous requirements. However, the space is already highly saturated and the banks are compelled to compete for their share within this market and achieve customer satisfaction and eventually accomplish a high level of loyalty in the long term.
The main management problem that banks in general encounter, is identifying the relevant steps that they need to accommodate, to maximize customer satisfaction levels in their operations.
1.3 Research aim
The aim of this research is to identify the factors which contribute towards achieving customer satisfaction. It is likely that there will be several areas that contribute towards customer satisfaction in the banking sector; however, this research endeavors to identify specific areas which contribute towards customer satisfaction in the banking sector of Sri Lanka.
Abarajithan and Abarajithan (n.d) have identified that the Sri Lankan banking sector remains competitive and therefore the banks require to develop a high level of customer satisfaction to ensure they achieve the appropriate results in the future. Meanwhile, the authors from the conclusions derived from the study, continue to argue that the banking sector of the country remains highly competitive by nature and therefore the banks require to concentrate on developing strategies which will enable the organization to become increasingly customer oriented. However, Wijetunga and Goonatillake (2003) have identified that whilst the main area of importance in the retail banking sector of the country is service orientation, it is disappointing to note that the Sri Lankan banks do not concentrate sufficiently on enhancing their level of service orientation, which is expected from them.
1.4 Research objectives
The following are the main research objectives that are associated with the study. These objectives contribute towards creating the framework that will provide insights related to the study aspects. It is important to identify the primary objective of the research along with the secondary objectives associated with it.
Primary objective:
To identify what are the factors which contribute towards customer satisfaction levels in banks of Sri Lanka. Whilst it is likely that there are several factors associated with this subject, the study endeavors to identify the main aspects and urge the banks to focus on these areas, which will subsequently enable them to improve the existing initiatives and ensure that customer satisfaction improves considerably, thereby guaranteeing the retention of customers and fulfilling the objectives of the bank.
Sub objectives:
- To ascertain the factors that contribute towards customer satisfaction in the commercial banking sector in general.
- To identify the customer expectations associated with each of these factors
- To measure the level of satisfaction, the customers associate with each of these factors
1.5 Research questions
The research questions that are identified below have been derived from the research objectives that are identified above. The research questions are as follows:
- What are the key factors that drive customer satisfaction in Business banks of Sri Lankan in general?
- What is the level of importance each factor is associated with, in the Business banking sector of Sri Lanka?
- What is the level of satisfaction each factor attracts, in association with the commercial banking sector of Sri Lanka?
- What are the key areas that need to be addressed, to increase customer satisfaction levels of Business banks in Sri Lanka?
The above research questions would provide the ground for the study to evaluate the main areas of importance in the context of improving customer satisfaction and how the banks could improvise these findings to enhance the customer satisfaction levels in the long term.
1.6 Significance
The Sri Lankan banks require to gain an in-depth knowledge of assessing customer satisfaction levels in terms of services. This will enable them to re-evaluate their current procedures and introduce improvements where necessary, to enhance the quality of services they offer to the customers in the future. This will assist the banking sector to be more stable and retain the customer base that each bank has acquired. Resultantly, the findings of the study will provide the banks with the required framework to identify the lapses in their current system and introduce remedial action, to improve the quality of the services that they provide to the market.
The study will also indicate the importance of each factor, which will contribute towards customer satisfaction levels. This will enable the banks to identify the key factors which impact customer satisfaction and initiate necessary action to improve these areas and assure the bank, the ability to keep their customers satisfied.
The study has a theoretical significance; the banking sector of any country is an important area and the factors that contribute towards the quality of the services will add to the body of knowledge which will be available for further research on this sector. Thus, the practical significance levels associated with this area remain considerably important and the parties will focus on gaining the appropriate results in this context.
The scope of the study includes collecting information from the customers of the bank regarding their level of satisfaction in terms of services. This exercise will be undertaken with the provision of a structured questionnaire. This will provide insight on the various measures the bank has currently undertaken, to ensure the customers remain satisfied, whilst it will also reveal what further measures that could be implemented, to maximize overall customer satisfaction levels in the future context. The recommendations are developed based on the findings of the study, which will enable the organization to determine what strategies one should consider, to improve customer satisfaction levels.
The key limitations for the study include sampling biases which could lead to inaccuracies in representing the total population. For instance, due to the quota sampling approach undertaken, the total population may not be appropriately represented, especially in terms of the smaller banks. It is also possible that some of the customers may be hesitant to discuss negative aspects regarding the banks that they are dealing with. Further, it is important to note, that the statistical approaches that will be used for analysis of data may comprise of several limitations and necessary action will require to be implemented, to ensure that the results derived are appropriate.
Chapter 2 – Literature Review
The literature review section is the section that highlights the studies that have been conducted in the past regarding customer satisfaction to understand how this aspect has impacted the banking sector in Sri Lanka. It is vital therefore, to implement necessary steps and achieve appropriate results, to maximize customer satisfaction in the banking sector. Meanwhile, there are several theories and models attached with this area of discussion and the literature review intends to briefly examine these aspects as well. Therefore, the literature review should provide clear insights to the subject and the concepts associated with the area of discussion.
2.1 Customer satisfaction
Banks are engaged in a commercial business and any business intends to develop a wider customer base and work with them, to ensure that they are satisfied. Therefore, companies require to identify what are the specific requirements a customer intends to fulfil, and work towards meeting these objectives. Thus, the long-term benefits of customer service and identification of market requirements remain high and the role of the banks also do not change in this backdrop (Munusamy, Chelliah and Mun, 2010). Meanwhile, the banks need to consider the satisfaction aspects of the customer and ensure that they work with the customers to provide them, with the required long-term benefits.
For instance, customers demand a certain set of services and products from a company; this is due to the specific needs that they possess. These specific needs would imply that the customers would require certain features associated with the products and the services they receive. Thus, the outcomes are likely to be positive by nature. Therefore, companies will require to ensure, they include the envisaged features to the products consistent with customer expectations (Bebli, 2016). If they fail in this regard, the customers are likely to reject the products and services they receive, from such companies. Resultantly, the companies will be unable to establish their reputation amongst the customers in the long-term.
This is applied in the instance of banks as well; resultantly, the banks will need to develop suitable features to the products and services. It is vital for the banks to undertake an in-depth evaluation to determine the exact products demanded by customers, and the associated features and cater to meet such requirements. These products and features will ensure that they reach appropriate benefits and increase customer satisfaction levels (Unyathanakorn and Rompho, 2014). Such an increase in customer satisfaction levels will benefit the parties in the future context and ensure the customers continue to remain with the bank they are associated with, in the long-term. Therefore, it is essential that the banks work towards identifying the exact requirements of the customers and ensure that they manage these areas consistent with market expectations (Belas and Jencova, 2014).
Therefore, long term benefits affiliated with customer satisfaction and maximization of the benefits are some of the key areas that requires attention, by the parties. It is evident that suitable benefits require to be provided to the customers when the banks develop features affiliated with the products and the services.
2.2 SERVQUAL Model
SERVQUAL model is one of the most commonly used models to measure service quality by the industry at present. The main theory behind the model is the fact that customers expect a certain level of benefits or a service quality while the organization provides them at a different level or perspective. This comparison indicates that there could be a gap between customer expectations and the product/service quality offered by the organization. Therefore, this is likely to lead to a mismatch in products/services offered by the organization, thereby leading to customer dissatisfaction. Thus, the model remains considerably useful in evaluating the quality of service (Handrinos, Folinas and Rotsios, 2015). The model however, analyze this scenario further and seek to identify the actual gaps in more detail.
This is one of the most commonly used models which highlight the sources of customer satisfaction. The customer, when transacting with a certain establishment for the provision of products and services, has a set of expectations from these elements. Therefore, whether the products and the services are likely to meet the needs of the customer is considerably important from a customer’s perspective. Meanwhile, customers evaluate these areas and ensure that appropriate steps are taken to maximize the benefits affiliated with these areas (Daniel and Berinyuy, 2010). This model indicates that if there are gaps between the customer expectation and the delivery of the service by the company, the organization is not able to entirely satisfy the expectations of the customers.
The model is a complex depiction of the reasons for the gaps that occur between customer expectations and the fulfilment of goods or services by the company (Kochan, 1992). However, when the companies have a clear understanding regarding this issue, it is possible that they will be able to provide precise solutions to the gaps that are in existence. This will enable them to reach appropriate results and benefit from these outcomes in the future (Handrinos, Folinas and Rotsios, 2015). Thus, the role of the model when it comes to identification of service quality gaps remains important. The model in detail can be illustrated as follows;
Figure 2.1 – SERVQUAL Model (Kozerska, 2007)
The above model depicts the five key areas of gaps that would contribute to the customer expectations being different to that of the overall services provided by the company (Kochan, 1992). Meanwhile, it is important that the companies identify the areas that the customers are dissatisfied with in terms of services rendered, and implement measures to mitigate the dissatisfaction levels. Such an approach will ensure that customer satisfaction is maximized and the areas that require improvements are addressed appropriately to fulfil market needs in the future (Daniel and Berinyuy, 2010). Therefore, the SERVQUAL model plays a prominent role, whereby it identifies the inconsistencies between customer needs and the offers made by the Company, to initiate remedial action.
Resultantly, an appropriate approach requires to be developed to understand the reasons which has led to the gap and subsequently implement remedial measures to close the gaps and meet the needs of these organizations in the future (Temba, 2013). The outcomes will maximize the benefits to the parties which will lead to positive outcomes in terms of achieving the appropriate objectives.
2.3 Key elements of customer satisfaction
The banks should be able to identify what the customers need and work towards these targets. It is possible that sometimes the banks will not be able to achieve the targets that are expected from them; however, they might be able to work towards optimizing a solution that will benefit the banks as well as the customers overall (Hoffmann and Birnbrich, 2012). Meanwhile, the research has provided different aspects as elements of customer satisfaction in the banking sector of the country. The following are some of the key areas that have been identified as important elements of customer satisfaction.
Role of the employees – the banking employees need to maintain a customer focused approach. This will provide an environment where customers will have the opportunity to discuss their issues and reach appropriate solutions. However, banking products in the modern context may be difficult to comprehend, and therefore providing an environment where the bank employee and the customer are able to discuss the viability of the product and proceed to sale, remain an important area of benefits (Murugiah and Akgam, 2015). Meanwhile, the employees should be equipped with a comprehensive knowledge regarding banking products provided to the customers and the associated benefits. They should also be able to work with the customers and identify the specific needs of the client and recommend the optimum product or service which best meets their requirements (Kochan, 1992). For instance, the customers might regard the bank employees as consultants in several instances and the employees should be prepared to satisfy the customers by providing appropriate insights regarding the products as well as the positives and negatives associated (Ogunlowore and Rotimi, 2015).
The employees will represent the bank and customer satisfaction remains an important area of services. The first impression regarding the capabilities of the bank is provided to the customers by the employees. Thus, the employees should be conversant in identifying customer needs, the ability to listen and understand and subsequently provide the client with appropriate solutions (Aldlaigan and Buttle, 2005). Therefore, possessing the appropriate capabilities and the ability to meet market demands are some of the important aspects that the employees should be equipped, when they provide solutions to the customers. Thus, the role of the employee remains vital to the bank and customer services.
The employees should possess a comprehensive knowledge regarding financial products and services; likewise, the employee should possess the ability to identify the specific needs of the customer and combine or tailor make the products and services offered by the bank to meet this requirement, and thereby win the confidence of the customer by offering the optimum solution (Dauda and Lee, 2016). The employees need to possess a service oriented nature; they should be able to identify the specific needs of the customers and ensure they cater to these specific needs (Alhemoud, 2010). The customers possess specific needs and the companies require to fulfil these needs consistent with expectations (Moutinho and Brownlie, 1989). The reliability of the employees requires to be high; as they need to ensure that the required services are provided in a reliable manner and gain the trust of the customer (Aldlaigan and Buttle, 2005) Meanwhile, in certain instances the employees are required to provide personal assistance. Therefore, the customers feel that they have received an exclusive set of benefits (Ahmad and Buttle, 2002).
The role of risk – The investors as well as the depositors of the bank undertake a certain amount of risk when they entrust their money with the bank. Meanwhile, the investment instruments contain a different level of risks and they will develop these instruments with investors who have different risk appetites in place (Naser, Jamal and Al‐Khatib, 1999). However, if an investor possesses a greater craving for risk this would eventually lead to the investments being able to earn a higher level of return in the future. Thus, risk requires to be managed consistent with the needs of the customers which will ensure that they receive products they need.
However, one of the key elements identified in managing of risk levels is to be fully transparent regarding the risk aspects with the management; therefore, the customers require to be aware of the level of risk they are likely to face. They should not be exposed to risks that they are unaware of (Ahmad and Buttle, 2002). Such an environment will provide the customer the opportunity to select a financial instrument with the appropriate level of risk, with which they are comfortable. Thus, the exposure of risk requires to be managed appropriately.
The banks will require to address mitigating of risks associated with investments (Ahmad and Buttle, 2002). Therefore, they need to evaluate the risk potential of the investments in a realistic manner and advice the customers (Dauda and Lee, 2016). Appropriate risk profiling will require to be implemented to ensure the optimum results are achieved (Alhemoud, 2010). Meanwhile, the risk appetite of investors differ and they are likely to seek various risk instruments based on the specific needs of the respective investor (Moutinho and Brownlie, 1989). Thus, the above aspects will ensure that the risks are managed appropriately. Likewise, it is also important to note that the market contains a certain level of rise and the bank should maintain the risks either on par or below the market risk levels.
The returns – This is one of the main areas of customer expectations; the customers invest money with the intention of earning a return, which is the reward they earn for the investment undertaken. Meanwhile, customers would generally seek instruments which generate a high level of return (Nagel and Cilliers, 1990). However, the main issue identified in such a situation being; that the returns are not determined, simply by the banks themselves. For instance, the return is linked to the economy of the country and the return generating capabilities of the banks will have a link to these aspects (Al-kayed, 2014). Thus, the banks will require to develop returns within the possible framework of the economic returns that can be generated.
Generally, the bank provides the customer with the rewards; therefore, it is possible that the requirements of the customers in terms of rewards may not be fully met, due to the limitations that exist as discussed above (Gilbert, 2000). Thus, the overall evaluation of needs in terms of rewards and catering to such requirements remain important in the future context. Therefore, it is the responsibility of the financial institution who are designated to provide appropriate rewards to the customer, to ensure that these rewards enable the parties to achieve suitable long-term outcomes in the future (Bebli, 2016). Resultantly, the role of the banks in providing rewards remains important.
The organization requires to ensure that they generate the expected returns consistent with investor needs; meanwhile, certain banking industry standards exist and the banks will need to generate returns consistent with these at minimum (Moutinho and Brownlie, 1989). Dauda and Lee (2016) state that the main requirement in this instance is to optimize the returns for the shareholders by the bankers. Likewise, Naser, Jamal and Al‐Khatib (2009) discuss that the risks and the returns require to be managed efficiently, if appropriate outcomes are to be achieved. The markets are expecting a certain level of returns whilst it is also important that the risks and the returns are balanced by the banks when they are offering financial products and services to the market.
Information – the banks require to implement relevant systems in place to provide customers with necessary information. The information requires to be comprehensive by nature and should contribute towards customer decision making capabilities. Therefore, the customers should be able to identify the optimum products and services whilst determine the benefits and issues associated with investing in such services due to the availability of the information base (Daniel and Berinyuy, 2010). Meanwhile, it is also important that the banks assist the customers to interpret the information and obtain an accurate picture of the scenarios involved.
However, if the parties are unable to receive the information in a timely manner from the bank, it is likely that prompt decisions will not be reached, and resultantly the customer will be exposed to undue issues. These issues may include incurring of losses, since they were unaware of the changes in interest rates as well as other aspects (O’Sullivan and McCallig, 2012). Thus, it is necessary that the banks inform the customers in a timely manner regarding the changes which has occurred in the market and the benefits as well as the issues that the parties are likely to be subject.
The information requires to be precise, when communicated to the customer, they require to be clear; this means they should be able to understand the information adequately (Moutinho and Smith, 2000). For instance, the customers should be in a position, to interpret the information in an appropriate manner; however, if it is misleading, it is likely that they will be unable to provide accurate information to the customers consistent with the expectations of the customers (Dauda and Lee, 2016). Meanwhile, the information requires to be updated reflecting the latest situations; for instance, the recent changes in the financial markets and the mechanisms to address these changes are important (Moutinho and Brownlie, 1989). Therefore, these updates require to be communicated to the customer on a regular basis (Alhemoud, 2010). Thus, the above features are identified as some of the prominent areas associated with information.
Variety – The discussion has previously indicated that customers are likely to possess different risk appetites. Therefore, bankers will require to develop various types of products, which will meet these changes in the risk appetite equation (Moutinho and Smith, 2000). Thus, the focus needs to be determined initially, to ensure that there are various products available to the customers enabling them invest in long-term or short-term orientation of the product; for instance, the parties might find it lucrative to invest in long term instruments, during stable periods of the economy. It is also possible that short-term instruments will be considered by the customers as well (Muffatto and Panizzolo, 1995). Meanwhile, loans and the investment opportunities are also two such areas of potential. Thus, these aspects should be taken into consideration when the banks develop the product portfolio. Therefore, in the event the customers are unable to provide such products, it is possible that the customers will be dissatisfied with the bank and eventually reach towards other alternatives to secure their requirements (Dauda and Lee, 2016). This will lead to the bank losing their customers, due to inadequacies in the product and services portfolio. This is another area for consideration.
The banks have a responsibility to provide an appropriate services portfolio which will cater to the needs of the customers; For instance, Ahmad and Buttle (2002) discuss that investors should be presented with suitable options such as deposit accounts and the variety needs to be high. Aldlaigan and Buttle (2005) stress on the need to offer different types of loan products; this will allow the customers to access the finances which suit the needs they possess. Meanwhile, Kaura (2013) believes that providing credit card facilities and related options will also lead towards making the offers of the banks attractive. Further, Dauda and Lee (2016) indicate that it is necessary to provide additional facilities to the clients in the future. All these aspects highlight that the banks will require to contribute to maximize the future benefits by introducing various activities.
2.4 Banking operations
The banking industry is one of the most competitive industries found globally; meanwhile, there are several banks which operate in a market and offering considerably similar services to the customers in the market. The banks have the responsibility of ensuring they provide an adequate return for the funds the customer either deposit with the bank or invest in various financial instruments (Høst and Knie‐Andersen, 2004). Likewise, the customers have certain expectations from the bank in relation to the products they provide as well as services. Therefore, the banks will have to identify these requirements and ensure that they meet these needs consistent with market expectations (Bena, 2010).
Most banks focus on commercial operations and hence described as Business banks. They offer the customers with a certain set of products. For instance, the customers will be able to invest in certain investment schemes (Sabir et al, 2014). For customers who are risk averse, they have deposit schemes which will enable them to invest in instruments, that have the capability to earn a minimum level of returns in the future. Moreover, the banks provide the customers with loans and various borrowing schemes (Kombo, 2015). For instance, Credit cards, Leases and other facilities are also included in this category of products.
Thus, the role of the banking industry remains vital to an economy; the role indicates that the banks will act as financial intermediaries. This in other words highlight the fact that the banks would invest in various forms of ventures and undertake the risk as well. This means that the banks will have to manage the risks and ensure that the deposit holders and the investors are only exposed to a level of risk that they have been apprised of (Borgqvist and Lindberg, 2011). This will ensure that the bank will manage the risks efficiently and lead to achieving positive benefits to the customers.
It is vital that the banking sector is considered an important player in the context of financial intermediation of the country. This in other words highlight the fact that banks require to manage their operations within the wider financial sector of the country in mind. Therefore, in the event issues are encountered with a bank, this is likely to lead to the exposure of the monetary dealings of the total financial sector of the country. To avoid such an occurrence, the sector remains stringently regulated (Hamzah, Ishak and Nor, 2015). The regulators will scrutinize the management of risks and ensure that the risks undertaken are appropriate and consistent with the needs and expectations of the market. This will enable them to establish the fact that they have avoided being exposed to high levels of risk in an undue manner.
2.5 Commercial banking in Sri Lanka
The banking sector of a country is important to conduct financial transactions; the banks play the role of financial intermediaries which facilitate the exchange of resources between parties. However, the factors that substantially impact customer satisfaction levels require to be identified and the gaps in these areas need to be analyzed to determine whether they require further improvement (Fraering and Minor, 2013). Meanwhile, there are several factors that are likely to contribute towards improving customer satisfaction levels and associated with the banking sector. However, all factors cannot be classified equally in relation to the level of importance, with every banking entity (Al-kayed, 2014).
Depending on the specific needs of the market, the importance of the factors that impact customer satisfaction requires to be identified and evaluated (Høst and Knie‐Andersen, 2004). Resultantly, the banking system of the country can subsequently ensure, that they provide solutions based on these specific areas that have been identified as being key, and provide appropriate solutions in terms of developing the banking sector of the given region (Fraering and Minor, 2013). Meanwhile, it is important to understand the level of services expected and the level of services that the parties are likely receive in this context.
Business banks offer the customers, returns for their transactions; therefore, the level of returns might be a factor that impact customer satisfaction at Business banks. The risk mitigation is another aspect that could lead to increased security with the investments. Likewise, service related factors such as the availability of branches, ATMs and other such facilities would also contribute towards customer satisfaction. Additionally, the capabilities of the employees in generating business as well as the financial performance areas of the bank could also contribute towards increasing satisfaction levels (Allred and Addams, 1999). Thus, there are several factors and the most important aspects associated with customer satisfaction require to be identified and prioritized, to improve the level of service.
SERVQUAL model indicates that there are certain expectations that are in place and the organizations will require to work towards fulfilling these requirements. Likewise, there are certain expectations that the customers envisage and the results they receive. Resultantly, this leads to a service quality gap; larger the gap, the lower the customer satisfaction levels will be (Ogunlowore and Rotimi, 2015). Therefore, the identification of the service gap could lead to identifying the level of customer satisfaction on each area and whether the customers affiliate a high level of interest. Thus, once the factors are identified, the extent of the gap associated with customer satisfaction needs to be scrutinized. This should be the basis adopted for developing proper strategies, which would lead to achieving positive results in terms of improving customer satisfaction levels of the commercial banking sector in the future (Hoffmann and Birnbrich, 2016).
2.6 Banking specifics
Meanwhile, it has been identified that the banking industry has certain specific requirements, which need to be taken into consideration, when they manage the services; resultantly, the industry is placed in a unique position and unlikely it could be managed, as a regular industry. The role the bank plays in managing the customer is considerably important as well, since the position they need to adopt is a significantly responsible stance, when managing the customers in the long term. Such an approach will benefit the market while ensuring all stakeholders will gain from the products and services they develop as well (Kaura, 2013).
The banking products provide a reward to the customer; it is generally understood that the customer will invariably be pleased to receive higher rewards. Therefore, the customers will demand for products which generate higher rewards to meet their needs. However, there is another aspect that requires attention namely; the risks (Alhemoud, 2010). Meanwhile, the risks are also bound to increase with the rewards; higher the risks taken, higher the rewards. Thus, the customers should be prepared to face issues in the context of the risk and reward balances in the future (Moutinho and Smith, 2000). This is one of the key areas that prohibits the banks from providing the customers with precise products and services that will match the requirements they envisage.
As discussed above, this is an industry which is controlled by stringent regulations; in other words, it is important for the parties to ensure that they adhere to the regulatory aspects and conform to compliance (Campbell and Finch, 2004). In the event the banks fail to comply with these regulations, they are likely to lose their licenses as well. This is another area of concern for the banks and they need to ensure that they work towards developing appropriate customer loyalty levels amongst these difficult conditions, that they may be compelled to face in the future (Ahmad and Buttle, 2002). Thus, these issues highlight the importance of the banking sector being positioned to develop outcomes consistent with market needs.
2.7 Construction of conceptual model
Thus, the above aspects assist to formulate the construction of the conceptual model of the discussion. The conceptual model in this context indicate the key elements associated with the study area and the related outcomes that will contribute to the results development. The study seeks to identify the main factors that would impact customer satisfaction levels in the context of the banking industry of Sri Lanka; it is vital therefore, to identify the appropriate elements and take necessary steps to ensure that relevant specifics are evaluated in each of these areas.
Figure 2.2 – The conceptual model of the study (Author developed)
Thus, the above conceptual model highlights the fact that the role of the independent variables remains vital in the management of the dependent variable, ie. the customer satisfaction levels. While these are factors that directly impact, based on past reports, it is possible that they are not applicable in the context of Sri Lanka. Thus, the study should highlight the main areas that are likely to impact the Sri Lankan context when the research is undertaken. Resultantly, the study should ensure that an appropriate stance is adopted to evaluate the key elements and reach an understanding regarding the nature of the outcomes related to each of these study areas.
2.8 Chapter summary
Therefore, the above discussion regarding previous work has revealed that the banking sector has some unique qualities which set aside the industry from the rest. The banks are compelled to consider several constraints instead of possessing the ability to freely market the products and services they promote. Resultantly, the industry requires to focus on providing appropriate benefits to the customers while operating within a regulatory framework that are assigned to them. This is a difficult area of operation and the banks will need to manage all these elements to reach long term beneficial results.
The discussion regarding the areas reveal that there are several elements that could impact the customer satisfaction levels; these include the employee focus, the risks and the returns of the financial instruments, variety of financial instruments and the information that are provided at appropriate times and in a timely manner to the customers.
Thus, the literature review has supported the appropriate development of the conceptual model; this will be the basis for the parties to reach appropriate long-term results and benefits from the outcomes in the future context. It is vital therefore, that the study develops the appropriate methodology with the view to evaluating the above conceptual model. This should indicate the nature of the relationships between the variables and how these will impact the overall industry. Therefore, the recommendations can be developed based on the findings of this study and these suggestions are likely to improve the customer satisfaction levels within the banking industry.
Chapter 3 – Research design and methodology
The section elaborates on the method the study was conducted and the results acquired. This should provide an understanding regarding the procedures adopted to improve the overall accuracy levels of the study and how these aspects have provided useful insights in the context of the practical relevance of the outcomes. It is evident that a study is likely to face various limitations and these restrictions impact the accuracy of the study outcomes. However, the development of the studies in this appropriate and accurate context will ensure that such issues are mitigated and appropriate outcomes are reached.
3.1 Research philosophy
The process of depicting the reality and evaluating the facts comprises part of the research process. Meanwhile, the reality requires to be interpreted consistent with the relevant facts that support the reality. Thus, defining an appropriate research philosophy in place is important and this should indicate how the facts of reality are being studied. For instance, constructivism is one of the research philosophies and this depicts the reality as a part of the social construct. In other words, this means that the whole society will collectivity work to develop reality and the understanding of this concept of reality. On the other hand, it is important to note the role of positivism in understanding of the reality surrounding us; the role of positivism highlights the fact that reality comprises part of the facts and evidence. In other words, studying the facts and the evidence available, should reveal the aspects of reality and the manner, in which, they are likely impact all parties.
In this instance, the focus on the facts and the evidences remain the basis for the research. For instance, the research requires to evaluate a social scenario and identify the resultant outcomes which have been reached. Thus, evaluating the evidences and reaching conclusions is the correct approach. Therefore, it has been concluded that the most relevant research philosophy in this instance, remains positivism for the study.
3.2 Research approach
The literature review should provide an understanding regarding the generic factors that are important to improve customer satisfaction levels with banks. The study will subsequently require to develop a conceptual mind map associated with these aspects and this will form the basis for the evaluation of the study outcomes. The conceptual mind map (which is identified in the literature review section of the study) will indicate the variables as well as the nature of the relationships that are identified in the case of the study. These relationships will provide the basis for evaluating the factors that influence customer satisfaction within the banking sector of the country.
Hypotheses are developed and they can be tested through this approach; which confirms that the approach is deductive by nature. This will provide results which are focused and consistent with the needs and expectations of the parties.
3.3. Study strategy
The study intends to identify the importance of each factor that contribute towards improving customer satisfaction levels in the commercial banking sector. Therefore, prominent factors require to be identified and suitable action implemented, to achieve accurate results. Thus, the significance of the gap and the contribution this makes towards customer satisfaction levels require to be identified. All these aspects indicate that the best approach for the study is quantitative by nature. This should provide details on the nature of influence these factors create on customer satisfaction. Meanwhile, the study encompasses information associated with five banks; this is similar, to a case study approach which is related to these five banks.
3.4 Data collection
This study will entail relevant data to be collected, which will provide insights to the area of the discussion. It is evident that the study requires to identify the nature of the relationships between the variables in consideration. Thus, the study should be quantitative by nature. An appropriate quantitative study approach is useful to identify the insights associated with the study area and use statistical models to evaluate the nature of the relationships.
The study concepts however, require to be operationalized to develop the appropriate field material. Therefore, to evaluate the relationships between the variables, the best approach is to use a structured questionnaire, which will enable one measure the outcomes of each scenario and ensure that a vision is developed consistent with the market needs in place. The following table highlights the operationalization of the variables for the study.
Table 3.1 – Operationalization of the variables (Author developed)
| Variable | Operationalization | Literature | Measure scale | Question number |
| Availability of information | Clarity and comprehensiveness | Moutinho and Smith, 2000 | Likert scale | Q1 |
| Interpretation | Dauda and Lee, 2016 | Likert scale | Q2 | |
| Frequency | Alhemoud, 2010 | Likert scale | Q3 | |
| Timeliness | Moutinho and Brownlie, 1989 | Likert scale | Q4 | |
| The employee focus | Knowledge | Dauda and Lee, 2016 | Likert scale | Q5 |
| Service focus | Alhemoud, 2010 | Likert scale | Q6 | |
| Customer needs | Moutinho and Brownlie, 1989 | Likert scale | Q7 | |
| Reliability | Aldlaigan and Buttle, 2005 | Likert scale | Q8 | |
| Personal assistance | Ahmad and Buttle, 2002 | Likert scale | Q9 | |
| Risks of investment | Mitigating | Ahmad and Buttle, 2002 | Likert scale | Q10 |
| Evaluation | Dauda and Lee, 2016 | Likert scale | Q11 | |
| Risk profiling | Alhemoud, 2010 | Likert scale | Q12 | |
| Risk vs. Market risk | Author developed | Likert scale | Q13 | |
| Variety | Moutinho and Brownlie, 1989 | Likert scale | Q14 | |
| Returns generated | Industry standards | Moutinho and Brownlie, 1989 | Likert scale | Q15 |
| Market needs | Author developed | Likert scale | Q16 | |
| Optimization | Dauda and Lee, 2016 | Likert scale | Q17 | |
| Risk and return balance | Author developed | Likert scale | Q18 | |
| Attractiveness | Naser, Jamal and Al‐Khatib, 2009 | Likert scale | Q19 | |
| Services portfolio | Deposits | Ahmad and Buttle, 2002 | Likert scale | Q20 |
| Loans | Aldlaigan and Buttle, 2005 | Likert scale | Q21 | |
| Credit cards | Kaura, 2013 | Likert scale | Q22 | |
| Wealth management | Author developed | Likert scale | Q23 | |
| Benefits | Dauda and Lee, 2016 | Likert scale | Q24 | |
| Satisfaction | Satisfaction | Aldlaigan and Buttle, 2005 | Likert scale | Q25 |
| Recommendation for deposits | Ahmad and Buttle, 2002 | Likert scale | Q26 | |
| Recommendation for loans | Author developed | Likert scale | Q27 | |
| Stability | Moutinho and Brownlie, 1989 | Likert scale | Q28 |
The above table indicates the variables and the nature of the relationships that these variables command with the elements of the questionnaire. This would highlight the insights related to the various aspects of the study and how they are linked with the questionnaire that has been developed. Following the operationalization process, it is vital that the hypotheses are developed. These should indicate the status of each area which requires to be tested through the study. Thus, the development of the hypotheses remains vital and ensures that the study remains focused on the area that the required information is being gathered. The following are the hypotheses affiliated with the study.
- H1 – adequate product information requires to be available for the customers regarding the products and the services of the bank to increase customer satisfaction levels
- H2 – high service orientation of the employees of the banks will increase customer satisfaction levels
- H3 – the risk of the investments requires to be lower for customer satisfaction levels to be high
- H4 – the returns generated requires to be high to enhance the overall customer satisfaction levels
- H5 – if the diversity of the portfolio of the bank is high, the customer satisfaction levels are likely to be high
Thus, the study will test the above discussed hypotheses, with the view to identifying the nature of the relationships between the variables. This will provide an indication of the main areas of influence, when customer satisfaction with the banks is being evaluated.
3.5 Sample selection
To conduct the interviews based on structured questionnaires, the customers of the banks need to be selected. The customers comprise of an appropriate group who are aware of the level of satisfaction they experience with the banks. While the population boundaries are clear, there is no clear way of developing a sample frame since the details of all the elements of the population cannot be ascertained. This makes it difficult to use a probability sampling based approach for the discussion. Thus, a non-probability sampling approach requires to be selected for the study. The study would select the five largest banks of the country based on the revenue earned in 2016 and select 20 respondents from each bank. The respondents are selected based on the contacts the researcher has established.
Thus, to select the banks, the study adopted quota sampling whilst to select the customers within the bank, the study engages convenient sampling approach. While random sampling would have produced somewhat an unbiased point of view regarding the discussion, it is vital to note that this is not possible since the customer details, were not provided by the banks.
There will be a total of 100 respondents who will be interviewed. Quota sampling method requires to be adopted since the size of the customer base of each bank is unclear. It is also beneficial to provide representation within the sample of members from each bank in an equal manner since the study endeavors to identify the market consensus rather than any specific point of view from customers of each bank. As the banks will differ from revealing their customer base to undertake any probability sampling associated with each bank; thus, an equal representation of the banks as well as the selection of the customers based on contacts should be an appropriate approach.
When the financial statements of the banks in 2016 were compared, the following list of banks have been identified as the first five banks based on the revenue that they have generated. Revenue generation capability stands to highlight the main banks that are operating in the market.
Thus, the above main banks that have been selected for the discussion. Meanwhile, from each bank, a quota of 20 customers were selected and the survey questionnaires were distributed to extract information. Therefore, the study is capable of covering a set of major banks and thereby enabling improved levels of generalization of the study findings, regarding the banking environment of the country.
3.6 Accessibility and ethical issues
It is important that the study selects the correct respondents to collect the data; however, it is also important to ensure that the respondents are comfortable with the study and they are in a position, to provide useful information consistent with the expectations they possess. It is important however, that the respondents are aware of the ability to abort the process any time if they feel embarrassed or find it difficult to provide the appropriate information. The purpose of the study and the other details are explained comprehensively to the respondents to create adequate awareness regarding the purpose of the study and ensure they possess a clear understanding regarding the reasons for providing information for the study. The questionnaire on the other hand will not contain any questions that will place the respondents in a difficult position to provide information.
3.7 Interview material
The background for the study requires to be developed and supported by an appropriate literature review. This would enable the conceptualization of the study and develop appropriate study material. Meanwhile, a structured questionnaire requires to be developed to gather the requisite information from the respondents. The structured questionnaire provides an appropriate method to facilitate the collection of quantitative information associated with the study areas. Likewise, to evaluate the importance and satisfaction levels of each attribute, a Likert scale based approach was adopted. This enhances the reliability and the validity of the findings.
The questionnaire is e-mailed to the selected respondents and a time for the interview is ascertained. Subsequently, the interviews were undertaken and relevant information collated, to meet the needs of the study. Interviews were held either over the phone or face to face where possible. However, the Online survey was not undertaken, since there was the possibility that certain clarifications may be required by the respondents. The collated information is thereafter analyzed and presented in the form of a comprehensive research report.
3.8 Data analysis methods
For the purposes of analyzing the data, the study requires to use appropriate statistical methods; these methods will enable the reaching of appropriate conclusions consistent with the needs of the outcomes. Frequency analysis is one of the methods that could be used to identify the primary objective. Subsequently, descriptive statistics can be used to evaluate the significant attributes. Therefore, mean scores were useful in comparing the significance level of each attribute in place. Meanwhile, correlation analysis was used for analyzing the relationships between the variables.
3.9 Limitations
The study encompasses several limitations in place as well; one of the main issues being, that the sample is unlikely to represent the appropriate population. This could imply that the selected sample does not have the ability, to represent the ideas of the population at large. Meanwhile, the study uses statistical analysis methods; these methods have their own limitations as well and the results are likely to represent inaccurate outcomes. It is also important to note that the respondents may not provide accurate insights regarding their respective banks and this could also impact the level of accuracy of the discussion.
Chapter 4 – Results, Analysis and Discussion
This is the section where the main findings of the study are highlighted. It is vital that appropriate insights are gained regarding the study areas and relevant benefits are reached by the parties. Possessing relevant insights is achieved by adopting appropriate methodology as well as adopting the correct approach towards data analysis. These aspects should indicate that outcomes could be reached in these areas. Therefore, an appropriate set of insights will require to be formulated, to reach relevant outcomes.
4.1 Demographics of the respondents
The respondents belong to various backgrounds; Therefore, it is important to identify the nature of the background that they belong to and whether they possess the capability of providing useful information. This assessment will be capable, of determining the credibility of the information that the respondents have provided and remains appropriate towards providing useful benefits in the future context.
4.1.1. Age
Age is a factor which is linked with the experience available in the markets. It is likely that individuals who are older would have worked with several banks and they would be able to provide suitable insights regarding their experience and the exposure they have gained in the banking sector. Therefore, the study requires to identify an appropriate mix of age groups as this will lead to reaching relevant insights, regarding the areas of work and the level of involvement with the banks.
Figure 4.1 – Age distribution of the sample (research data)
The above table indicate that there is a fair mix of ages within the group of respondents. Resultantly, they will be able to provide useful insights regarding the areas under consideration and achieve appropriate results in the future. Therefore, the insights provided by the study are likely to be able to generalize the facts in a suitable manner and achieve the intended results.
4.1.2. Education level
Meanwhile, the sample should represent people at different education levels. This is owing to the need for all levels of education to be represented in the sample which is adopted for discussion. Therefore, possessing an appropriate mix of education levels will contribute towards the possibility of generalizing the findings of the discussion. The following chart indicates the details of the education levels of the respondents.
Figure 4.2 – Education level of the respondents (research data)
The above chart depicts that the findings of the study represents the views of a considerably educated group of persons, who are positioned to reach valid conclusions. Therefore, the insights provided in the context of the study could be used for generalization, due to the representation of the education levels of the group within the sample selected.
4.1.3 Employment
This is another area that could impact the banking habits of the people. It is important that the study represents a diverse set of respondents who will be able to provide useful insights regarding the activities of the banks they transact with, whilst the nature of employment and income of the respondents will reveal, the specific financial requirements the parties are likely to envisage. The following chart indicates the details associated with the level of employment of the respondents used for the study.
Figure 4.3 – Employment categories (research data)
The above chart indicates that there are several parties involved; while there is a minority group of respondents who are unemployed, the majority of the respondents are employed and earning decent revenues which they are likely to consider for investment. Therefore, the above respondents are suitably positioned to provide useful insights regarding banking facilities and the issues they encounter with these aspects.
4.1.4. Gender
It is important to ensure that gender is represented fairly within the sample. This will ensure that any gender related issues will be addressed and represented through the sample and discussions involved, which will subsequently lend to long-term outcomes. In this instance, the gender biasness is towards the male population representing 61% whilst the balance comprises of female respondents. However, it is important to note that there is a fair representation of the genders within the sample and this ensures that any gender related biasness is eliminated within the responses provided by the respondents.
4.1.5. Length of usage of the bank
Meanwhile, based on the duration a respondent has utilized the services of a particular bank, it is apparent that they will be able to provide useful insights regarding the overall operations as well as convey how successfully the bank has met the needs of the parties. However, if the customers have used the services of a bank for a longer duration, this highlights that the customer possesses a high level of loyalty towards the bank. Thus, an appropriate mix of periods will also be considerably important.
Figure 4.4 – Length of usage of the banking services (research data)
The above chart depicts that there is a mix of people who represent different durations of conducting transactions with the bank and thereby positioned to provide significant insights. Thus, respondents possessing an appropriate period of transactions with the bank, remains considerably useful, since their experiences with the bank will enrich the findings, as they describe their positive encounters with the bank.
Thus, the above discussion associated with the demographics of the study indicate, that the sample has a fair mix of respondents who are equipped to provide useful insights regarding banking aspects and related information. The main purpose of the study is to identify the nature of the banking habits that they possess whilst determine the satisfactory levels derived from the usage of these banking services.
4.2 Main areas of findings
These are the primary findings of the study which highlight the core areas associated with the study discussion. Meanwhile, the insights of the study remain considerably important since it highlights the benefits that they will achieve. Thus, the focus on the key areas of the discussion also remains vital and appropriate insights can be formulated related to these aspects.
The study utilizes Likert scale readings in its analysis; for each attribute, and scores are provided based on levels agreed by the customer. Higher the agreement levels, higher the score. The highest score of 5.0 was recorded, whilst the lowest score was represented at 1.0. This will enable one to average the scores which have been received, for each attribute of the study. Thus, the eventual results will allow comparison of these scores and quantification of the overall mean scores received by the variables in consideration.
4.2.1. Information
The banks are compelled to provide existing customers and potential customers with relevant information that they require; since receiving appropriate information will enable them to reach suitable decisions. The information needs to be accurate and easily understood. Likewise, the information should be delivered in a timely manner, as it will enable effective decision making. These are some of the key areas of consideration when information related aspects are taken into consideration.
Figure 4.5 – Information availability (research data)
The above chart depicts that the timeliness of the information is high; since the banks are providing the customers with information promptly, to effect appropriate decisions regarding investments they intend reaching in the future. On the other hand, the banks will be prepared to interpret this information and areas where such attention and clarity are required. Thus, the above aspects require to be considered, when information related aspects are taken into consideration.
However, it is important to note that clarity and the comprehensiveness of the information is an area which requires an appropriate level of improvement. For instance, the information currently available may not be clear or sufficiently comprehensive to reach appropriate decisions. On the other hand, the banks may be incapable, to provide relevant information regarding the various changes which occur in the financial world and likely to impact the outcomes applicable to customers. This is another area which the banks require to concentrate, on improving in the future.
4.2.2. Employees
The employees play a vital role in improving customer satisfaction, based on the literature that has been discussed. For instance, the customers are reliant on the information provided by the employees as they continue to work with the employees to reach desired results in the future. The following chart depicts details regarding the employees and the service scores that they received in these areas.
Figure 4.6 – Employee services (research data)
The overall scores received by the employees are high; the fact that all have received scores above 3.00, and this highlights the fact that the role of the employees is a factor that contributes to the customer satisfaction. Understanding precise customer needs and providing services to suit these requirements including personal assistance provided to customers are some of the main areas of focus.
There are hardly any negative aspects that can be identified through the discussion; despite reliability of the employees was the least scoring attribute, it is important to note that the score that has been received by the attribute remains high. Therefore, since the overall scores that have been received by this variable has been high, thereby confirming that the overall reliability associated with the employees of the company remains high. Thus, the role of the employees has been a factor that contributes to the banks in a positive manner and could be considered the link between the customers and the banks which requires to be improved due to the role played by the employees.
4.2.3. Risk
This discusses the level of risk that investors will undertake when considering investments through a bank. The banks will require to provide the investors with varying instruments which attach different levels of risk. Meanwhile, depending on the appetite they possess towards risks, a decision will be undertaken regarding the selection of a financial instrument. It is very likely that they will have to maintain different risk portfolios and ensure that the desired outcomes are reached by the parties in the future. However, if the banks disregard the risk levels, it is very likely that the investors will find themselves exposed to undue levels of risks and issues in the future.
Figure 4.7 – Risk management (research data)
The above risk portfolio indicates that the general perception regarding banks negotiating risks remain positive; for instance, the variety of the instruments available and the levels of risk the bank exposes the investors compared with the market risk, indicate that the investors have been satisfied with the risk that they have encountered. However, it is also important to note that the risk mitigating steps have received the lowest score. This highlights that while the banks have undertaken necessary steps to mitigate the risks, there is room for further improvement by the bank towards this initiation.
It is however, important to note that the majority are of the view that the banks manage the risk levels at a lower point, when considering the general market risk associated. It is also important to note that several customers were satisfied with the variety of risk aspect related products currently available for investment. This will ensure that potential investors will be able to reach appropriate benefits by the returns generated in the future.
4.2.4. Returns
The banks would have to ensure that they provide the investors with the expected returns; meanwhile, the investors are of the view that they will be able to achieve appropriate returns by selecting suitable investment instruments. Thus, the role of selection of appropriate investments remain important to ensure generation of positive returns in the future. Therefore, developing the ability to generate appropriate returns are important to banks, to achieve suitable results in the future.
Figure 4.8 – Returns generation (research data)
The above chart depicts that the generation of returns based on market needs is an area which has not been developed to expected levels; in other words, the investment options offered by several banks, fall short of the return expectations of the market. Thus, the actual level of attraction of these investment options remain limited to the investors. Meanwhile, several investors are of the view, that the returns they earn from the banks do not justify the level of risk that they are exposed to; this remains another critical area which requires to be addressed by the banks, to reach conclusive decisions.
It is however clear that the banks have been able to ensure the returns they provide, remains consistent with the industry standards which currently exist. Therefore, it is likely that the industry standards do not conform with the expectations of the markets. However, it is apparent the banks should endeavor to optimize the return generation capabilities of the investment options that are currently available, which has already been brought to the notice of the banking industry, by several parties. This ensures that the return generating capability is one of the key areas of concern and the banks need to improvise mechanisms, to optimize these aspects with the view to reaching positive results.
4.2.5. Portfolio
Maintaining an appropriate portfolio is one of the key requirements the bank needs to address, to ensure the customers remain satisfied. Customers are likely to possess different requirements and expectations. Therefore, maintaining a wide variety of products will enable the bank to cater to these different requirements from one destination. Thus, the long-term benefits associated with these areas are likely to be high. It is vital that the banks evaluate the variety of requirements that are envisaged by the customers and cater to these needs consistent with market expectations.
Figure 4.9 – Portfolio development (research data)
From the readings of the above chart it is apparent, that one of the weak areas identified is the wealth management; whilst the banks may have generated various wealth management options, they have been unsuccessful in linking the customers to these options consistent with the needs they envisage. Further, the criteria of other benefits have also received lower scores. Thus, the banks need to evaluate the benefits of wealth management and identify how these features can be promoted amongst the customers, to achieve appropriate benefits thereof.
However, the banks have been able to meet the demands of the customers in various other areas which represent some of the commonly used products and services. The deposits for instance remains one such area; it is also important to note, that the banks are positioned to offer several types of loans as well. Meanwhile, the role of credit cards also remains an area of importance to the parties. Thus, these three areas have been contributing at satisfactory levels and offering appropriate services consistent with market needs. It is important to improve the portfolio related products and continue to attract more investors and customers to invest in the services of the bank.
4.2.5. Customer satisfaction
Customer satisfaction is the dependent variable of the study; this shows the main area that the study eventually seeks to evaluate based on the relationships that are in place. Meanwhile, it is apparent that if an appropriate level of customer satisfaction is prevalent, it is possible to achieve suitable results consistent with market needs. Therefore, when customers are satisfied with a product or a service, it is evident that they will purchase the given product or service with the knowledge that they are likely to be able to enjoy the benefits they envisage.
Figure 4.10 – Customer satisfaction (research data)
The customer satisfaction levels in relation to the services provided by the banks have also been maintained at a considerably high level. Resultantly, the banks have been able to develop certain products and services which suit the requirements of the customers. However, it is also important to note that there could be other aspects which require to be identified in terms of the impact it creates, on the level of customer satisfaction in the future. Therefore, such aspects and the related outcomes are likely to be beneficial in achieving appropriate results.
It is evident that the customers have scored high, in terms of the stability of the banks; therefore, the banks are suitably positioned to continue to offer the customers with services, that are regularly demanded from the banks. Thus, the stability of the banks remains an important area, since it assures the customer that the position of the bank is considerably stable. It is also important to note that they are willing to recommend the deposits as well as the loan facilities offered by the banks. However, the overall satisfaction levels possess room for further improvement and it is evident that the impact of various other aspects may have had a detrimental effect on the ratings.
4.2.6. Evaluating the relationships
The above-mentioned discussions continue to emphasize that the banks are seeking to maintain a high level of services to the customers. While there are several areas which require improvement, there are many other areas that have provided the customers with a considerably satisfactory level of services and seek to ensure that they are benefitted. It is evident that the banks have been able to maintain high levels of customer satisfaction with the products and the services that they have offered to the market. However, it is yet to be proven whether these products and services have eventually contributed towards customer satisfaction levels.
Meanwhile, correlation analysis has been adopted, to evaluate the nature of the relationships between the variables, since it is recognized as the best approach. Correlation analysis will not only indicate whether a relationship exists, but will also highlight the nature of the relationship. Likewise, it will also display the nature of the relationship, existing between these variables and whether the relationship is positive or negative. If the relationship is positive, this position will be signified by the increase of the independent variable, whilst the dependent variable will also increase. However, in a situation of a negative relationship, with the increase of the independent variable, the dependent variable would decrease.
Table 4.1 – Correlation scores (research data)
| Information | Employees | Risk | Rewards | Portfolio | |
| Satisfaction | 0.67 | 0.85 | 0.24 | 0.75 | 0.54 |
The above table describe the nature of the relationships between the variables in consideration; it is evident that availability of the information is one of the aspects which contribute positively towards customer satisfaction. Therefore, a score of 0.67 indicates that with the increase in the availability of customer information, it is very likely that the satisfaction levels associated with the financial institutions will continue to increase as well.
When the variable in relation to employees are considered, a score of 0.85 has been achieved, which depicts that the relationship between employees and the level of satisfaction, is significantly close. Thus, this implies that the employees are considerably service oriented, and one could conclude that the customers are likely to be satisfied with the level of services they receive. This depicts the importance of the role of the employees. Further, the role of the rewards is also high with a correlation score of 0.75 since maintaining a wide portfolio also contributes to customer satisfaction levels. Thus, the above aspects remain significant areas of importance.
However, it is evident that the risk and satisfaction levels do not portray a clear relationship; the score of 0.24 is significantly low to reach a conclusive decision regarding the relationship between the variables in consideration. Therefore, risk being an intangible element might not directly impact the overall customer satisfaction levels of the banks. Resultantly, the above area remains one of the important aspects which can contribute significantly towards, appropriate benefits in the future. Therefore, the above findings will formulate the basis for the hypotheses testing. This will enable reaching of conclusive results in the hypotheses.
4.3 Hypotheses results
It is vital that the hypotheses of the study undergo testing; the testing results are based on the correlation analysis related findings. The key areas of consideration and the results obtained by the parties could be highlighted as follows:
- H1 – adequate product information requires to be available to customers regarding the products and services of the bank, to increase customer satisfaction levels – proven
- H2 – Possessing a high level of service orientation by the employees of the banks, will invariably contribute towards customer satisfaction levels – proven
- H3 – the risk of the investments requires to be lower, for customer satisfaction levels to be high – proven
- H4 – the returns generated requires to be high, to enhance the overall customer satisfaction levels – proven
- H5 – if the diversity of the portfolio of the bank is high, the customer satisfaction levels will also be high – proven
Thus, the above aspects associated with the hypotheses indicate that the results are proven to a certain extent and appropriate benefits are reached by the parties owing to these relevant aspects of achievements. Therefore, the above aspects conclude the sufficient availability of information, returns generated, variety of the products and employee service orientation are key areas which contribute towards improving customer satisfaction levels.
Chapter 5 – Discussion and conclusion
5.1 Discussion
The literature review of the study has highlighted that previous studies have contributed immensely towards useful insights regarding factors, which have a bearing on customer satisfaction levels with the banks. This is a specific sector where explicit factors require to be in place to ensure that the customers are satisfied (Borgqvist and Lindberg, 2011). Meanwhile, it is also evident that customers can change their preference in banks with minimum issues whilst the bankers possess significantly low potential to differentiate their products and services on offer.
Meanwhile, the literature review has identified the role of customer satisfaction to be considerably important as there are only a minimum number of avenues for the banks to develop their competitive edge over their competitors. However, it is also important to note that most of the transactions of the bank, involve the trust of the customers and if they can develop a high level of customer trust, they will be able to reach beneficial results in the future (Hamzah, Ishak and Nor, 2015). The long-term loyalty is a result of this trust and customers believe that such banks will provide them with positive outcomes in the future.
One of the important aspects of consideration is the ability of the bank to provide the customers with necessary information, to effect suitable investment decisions. Therefore, when customers are in possession of the relevant information, it is likely that they will be able to reach appropriate benefits and achieve positive results in the future (Munusamy, Chelliah and Mun, 2010). Thus, the customers will identify the products and services the bank offers, which will suit their specific requirements and select the appropriate portfolio. This will enable them to enhance the benefits they receive from the banks in the future.
It is also important that the employees remain considerably service oriented by nature; this highlights the fact that the role of the employee and service orientation are affiliated and play a vital role in achieving appropriate benefits in the future (Unyathanakorn and Rompho, 2014). Further, the risk and the reward aspects naturally comprise part of the service portfolio of the banks and likely to impact the overall employee satisfaction levels. Therefore, the banks will require to develop product portfolios which will successfully meet the requirements of the markets and ensure that the customer benefit from the variety that they are likely to receive (Daniel and Berinyuy, 2010).
Meanwhile, the findings of the study did not contradict most of the areas in consideration. Therefore, it is relevant for appropriate steps to be incorporated, to improve overall customer satisfaction through these areas. The study however has not identified the direct importance of the risk factor which is associated with the parties to reach appropriate benefits in the future. However due to regulatory issues, this is an area which the banks will be unable to ignore. Thus, it is important for the parties to work towards ensuring appropriate results are reached consistent with market needs and eventually benefit from these outcomes.
5.2 Recommendations
The following recommendations have been developed however, to ensure that the areas which require attention and improvement are addressed appropriately in the future.
- The banks have not yet addressed the issue regarding clarity of information provided; and it is vital that the information is of superior quality, which will have a considerable impact on the investment decisions undertaken by customers. Thus, possessing appropriate and quality information, is paramount for the respective parties to achieve relevant results.
- The banks require to ensure that they develop the options to serve the needs consistent with market expectations. It is apparent that the industry standards remain below market expectations but interestingly several banks have successfully provided benefits on par with the standards. It is likely that this approach ensures the parties would eventually reach a clear set of products and services which will command a higher level of risk affiliation, whilst improve the return generating capability of the bank. This will provide positive outcomes in terms of return generation improvement to customers who seek such options.
- The bank requires to ensure that they provide the requisite information regarding the products and the services in a timely manner. This will ensure that the parties are equipped with the relevant information in a timely manner, which will enable them to use the information in the most effective manner to achieve the desired outcomes in the future. Thus, the bank will benefit from the increased customer trust regarding the bank activities and improved levels of loyalty associated with the outcomes.
- The customers have identified that most products offered by the bank are unattractive; since most banks offer similar products which are unlikely to meet the expectations of the customers. The customers have specific needs based on their profession and the lifestyle that they are engaged with and the banks are likely to change the product aspects to meet these requirements and fulfil the exact requirements of the market.
5.3 Conclusion
It is apparent from the above discussion that banks are required to develop the products and solutions which will precisely meet market requirements. Whilst in most instances, the banks have been able to meet the requirements of the markets, this does not imply that the solutions offered have been perfect and consistent with actual market requirements of the future. It is further important that they will be able to achieve positive results that will lead the parties to achieve appropriate long-term benefits in the future.
The study has been able to guide the banks to identify the nature of the products and services they provide and the benefits that the parties will be able to receive due to the usage of these products. With increased market focus and the service orientation, the banks will be able to meet the exact requirements of the customer in the future.
References
Abarajithan, J.W. and Abarajithan, A.N., (nd.). A study on the customer orientation of the Sri Lankan Banking Sector. Journal of Social Sciences – Sri Lanka. [pdf] Available at:<http://repository.kln.ac.lk/bitstream/handle/123456789/11022/26.pdf?sequence=3&isAllowed=y, [Accessed on: August, 2017].
Ahmad, R. and Buttle, F., (2002). Retaining telephone banking customers at Frontier Bank. International Journal of Bank Marketing. Vol. 20, Issue: 1, pp.5-16.
Aldlaigan, A. and Buttle, F., (2005). Beyond satisfaction: customer attachment to retail banks. International Journal of Bank Marketing. Vol. 23, Issue: 4, pp.349-359.
Alhemoud, A.M., (2010). Banking in Kuwait: a customer satisfaction case study. Competitiveness Review: An International Business Journal. Vol. 20, Issue: 4, pp.333-342.
Al-kayed, W., (2014). Service Quality and Customer Satisfaction in Cairo -Amman bank -in Jordan. American International Journal of Contemporary Research. Vol: 4, No.4; April 2014. [pdf]. Available at:<http://www.aijcrnet.com/journals/Vol_4_No_4_April_2014/13.pdf,> [Accessed on: August, 2017].
Amoah-Mensah, A., (2010). CUSTOMER SATISFACTION IN THE BANKING INDUSTRY: A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF GHANA AND SPAIN. [pdf]. Available at:< http://www.tdx.cat/bitstream/handle/10803/22657/taam.pdf;sequence=3,> [Accessed on: August, 2017].
Asher, M., (1989). Measuring Customer Satisfaction. The TQM Magazine. Vol. 1, Issue: 2.
Bebli, R.S., (2016). The Impact of internet banking service quality on customer satisfaction in the banking sector of Ghana. [pdf] Available at:<http://www.diva- portal.se/smash/get/diva2:833400/FULLTEXT01.pdf,> [Accessed on: September, 2017].
Belas, J. and Jencova L., (2014). Reasons for Satisfaction and Dissatisfaction of Bank Customers. Study from Slovakia and Czech Republic. International Journal of Entrepreneurial Knowledge. Vol, 2, Issue 1, pp 4-13.
Bena, T., (2010). Evaluating Customer Satisfaction on Banking Services. Management & Marketing (2010) Vol. 5, No. 2, pp. 143-150.
Borgqvist, J. and Lindberg, D., (2011). Customer involvement in service innovation – a study of the bank industry. [pdg]. Available at:<http://lnu.diva-portal.org/smash/get/diva2:428172/FULLTEXT01.pdf,> [accessed on: September, 2017].
Daniel, C.N. and Berinyuy, L.P., (2010). Using the SERVQUAL Model to assess Service Quality and Customer Satisfaction. [Online] Availalbleat at: <http://www.diva-portal.org/smash/get/diva2:327600/fulltext01>, [Accessed on: September, 2017].
Dauda, S.Y. and Lee, J., (2016). Quality of service and customer satisfaction: a conjoint analysis for the Nigerian bank customers. International Journal of Bank Marketing. Vol. 34, Issue: 6, pp.841-867.
Fraering, M. and Minor, M. S., (2013). Beyond loyalty: customer satisfaction, loyalty, and fortitude. Journal of Services Marketing. Vol: 27, Iss: 4 pp. 334-344.
Gilbert, G.R., (2000). Measuring internal customer satisfaction. Managing Service Quality: An International Journal. Vol. 10, Issue: 3, pp.178-186.
Hamzah, N., Ishak, N.M. and Nor, N.I.M., (2015). Customer Satisfactions on Islamic Banking System. Journal of Economics, Business and Management. Vol. 3, No: 1, January 2015.
Handrinos, M.C., Folinas, D. and Rotsios, K., (2015). Using the SERVQUAL model to evaluate the quality of services for a farm school store. Journal of Marketing and Consumer Behaviour in Emerging Markets. Vol. 1, Issue: 1, pp 62-74.
Hoffmann, A.O.I. and Birnbrich, C., (2016). The impact of fraud prevention on bank‐customer relationships: An empirical investigation in retail banking. International Journal of Bank Marketing. Vol: 30, Issue: 5, pp.390-407.
Høst, V. and Knie‐Andersen, M., (2004). Modeling customer satisfaction in mortgage credit companies. International Journal of Bank Marketing. Vol. 22, Issue: 1, pp.26-42.
Kaura, V., (2013). Antecedents of customer satisfaction: a study of Indian public and private sector banks. International Journal of Bank Marketing., Vol. 31, Issue: 3, pp.167-186.
Kochan, A., (1992). Defending customer satisfaction. The TQM Magazine. Vol. 4: Issue: 3.
Kombo, F., (2015). Customer satisfaction in the Kenyan banking industry. Journal of International Studies. Vol. 8, No: 2, 2015, pp. 174-186.
Kozerska, M., (2007). MANAGING SERVICE QUALITY – SERVQUAL METHOD:
STRENGTHS AND WEAKNESSES. Advanced Logistic Systems. pp 61-65.
Moutinho, L. and Brownlie, D.T., (1989). Customer Satisfaction with Bank Services: A Multidimensional Space Analysis. International Journal of Bank Marketing. Vol. 7, Issue: 5, pp.23-27.
Moutinho, L. and Smith, A., (2000). Modelling bank customer satisfaction through mediation of attitudes towards human and automated banking. International Journal of Bank Marketing. Vol. 18, Issue: 3, pp.124-134.
Muffatto, M. and Panizzolo, R., (1995). A process‐based view for customer satisfaction. International Journal of Quality & Reliability Management., Vol. 12, Issue: 9, pp.154-169.
Munusamy, J., Chelliah, S. and Mun, H.W., (2010). Service Quality Delivery and Its Impact on Customer Satisfaction in the Banking Sector in Malaysia. International Journal of Innovation, Management and Technology. Vol. 1, No. 4, October 2010, Vol, No, pp 398 – 404.
Munari, L., Ielasi, F. and Bajetta, L., (2013). Customer satisfaction management in Italian banks. Qualitative Research in Financial Markets. Vol. 5, Issue: 2, pp.139-160.
Murugiah, L. and Akgam, H.A., (2015). Study of Customer Satisfaction in the Banking Sector in Libya. Journal of Economics, Business and Management. Vol. 3, No. 7, pp 674-677.
Nagel, P.J.A. and Cilliers, W.W., (2009). Customer Satisfaction: A Comprehensive Approach. International Journal of Physical Distribution & Logistics Management. Vol. 20, Issue: 6, pp.2-46.
Naser, K., Jamal, A. and Al‐Khatib, K., (1999). Islamic banking: a study of customer satisfaction and preferences in Jordan. International Journal of Bank Marketing. Vol. 17, Issue: 3, pp.135-151.
O’Sullivan, D. and McCallig, J., (2012). Customer satisfaction, earnings and firm value. European Journal of Marketing. Vol. 46, Issue: 6, pp.827-843.
Ogunlowore, A. J. and Rotimi, O., (2015). Analysis of Electronic Banking and Customer Satisfaction in Nigeria. European Journal of Business and Social Sciences. Vol: 3, No.3, pp 14 – 27, June 2014.
Sabir, I.R., Ghafoor, O., Akthar, M., Hafeez, I. and Rehman, A.U., (2014). Factors Affecting Customer Satisfaction in Banking Sector of Pakistan. International Review of Management and Business Research. Vol. 3, Issue.2, pp 1014 – 1025.
Temba, M.L., (2013). The Assessment if Service Quality and Customer Satisfaction Using SERVQUAL Model; A Case Study of Tanzania Telecommunications Company Limited (TTCL). [pdf]. Availalble at:< http://repository.out.ac.tz/937/1/marry_temba.pdf>, [Accessed on: September, 2017].
Unyathanakorn, K. and Rompho, R., (2014). Factors Affecting Customer Satisfaction in Online Banking Service. Journal of Marketing Development and Competitiveness. Vol 8, Issue 1, pp 50-60.
Vukmir, R.B., (2006). Customer satisfaction. International Journal of Health Care Quality Assurance., Vol. 19, Issue: 1, pp.8-31.
Wijetunga, D. and Goonatillake, R. (2003). Customer satisfaction in Sri Lankan retail banking: The role of service quality. Sri Lankan Journal of Management.
8 (3&4),172-194.
Work in Sri Lanka. (2017). Banking and Finance Industry. [Online]. Available at:< http://workinsrilanka.lk/living/banking-and-financialservices-industry-in-sri-lanka/,> [Accessed on: August, 2017].
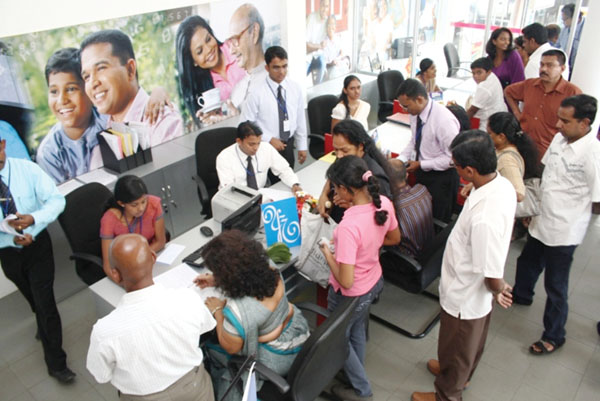


One comment