Introduction
Today, in comparison to conventional foods, the demand for organic food products has drastically escalated, on a global scale. The primary two justifications for the latter, owes to rising consumer awareness on the detrimental impact of consuming toxins, and the contemporary fad of eating healthy.
Thus, for the purpose of this assignment I will take into consideration a hypothetical organization, which is operating in the Organic food Industry. As this paper progresses, I will provide a comprehensive analysis of the potential to expand into overseas markets, as requested by the management of the said hypothetical organization.
1. External and Internal analysis of the selected three countries.
I will analyse the potential of the organic food industry, for the three nations; Canada, Singapore, and China. The analysis will be conducted by comprehensively assessing the internal, and external environment by employing two analytical tools; PEST, and SWOT analysis.
Canada
SWOT Analysis
Strengths
- Strong fiscal policies, and robust financial sector. The latter is the key justification as to why Canada was capable of recovering from the 2008 recession, relatively quickly in comparison to other nations. (Lane, 2014)
- The Canadian banks are ranked among the best in the world according to the World Economic Forum.
- Canada has substantially benefitted from the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), enabling the country to enjoy a considerable trade surplus. (“The World Factbook: Canada ”, 2017)
- Significant entrepreneurial support offered by the Canadian government, enabling one to benefit from tax reductions, and breaks.
Weaknesses
- Canada’s substantial dependency on the United States as a “trading partner”. A considerable sum (74.5%), of the nations exports is sent to the United States, whereas the United States imports a mere 14.1 % from Canada. Thus, this dependency had a significant toll on Canadian export market following the recession. (Lane, 2014)
Opportunities
- The Canadian market offers tremendous opportunities, particularly in the organic food market. In comparison to other agro foods, the Canadian organic food market has tripled since 2006, and is valued at over“ $ 3.5 bn per year in sales.” (Mackinnon, 2013)
- increasing government regulations on Agro foods, the promotion of organic food, and increasing consumer awareness on the benefits of consuming the latter provides tremendous opportunity for new investors in this sector.
Threats
- The EU debt crisis serves a potential threat to the Canadian economy.
- The FTA between Canada and Europe can be detrimental to Canada owing to the economic stagnation of Europe.
- New entrants will face a substantial threat from existing local firms, “The organic market in Canada has also grown exponentially over a very short period, to the point that it is now the fourth largest in the world.” (Mackinnon, 2013)
PEST Analysis
Political Factors
The Canadian government is a democracy, consisting of a “parliamentary government.” Canada can be credited for engaging in numerous free trade agreements, which will contribute towards the enhancement of its economy, “facilitate bilateral free trade, avoid double taxation, protect foreign investment, strengthen financial and banking institutions, and assist development.” (“Canada”, n.d.)
Economical Factors
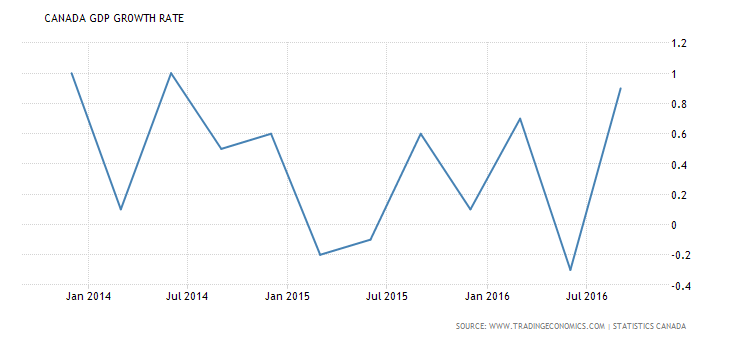
Not only is Canada among the worlds wealthiest nations, the Canadian economy can also be credited for being among the world’s best performing. It has the world’s 10th largest economy in terms of nominal GDP, and 15th largest in terms of Purchasing Power Parity. Furthermore, it is also among the group of G-7 nations. (“Canada Economic Forecast”, 2017)
Illustrated below are Canada’s key economic indicator as of 2017;
GDP (USD,billion) 1551
GDP growth (%) 0.9
GDP per capita(USD) 50001
Unemployment Rate (%) 6.09
Inflation Rate (%) 1.5
Interest Rate (%) 0.5
Source : National Bureau of Statistics Canada
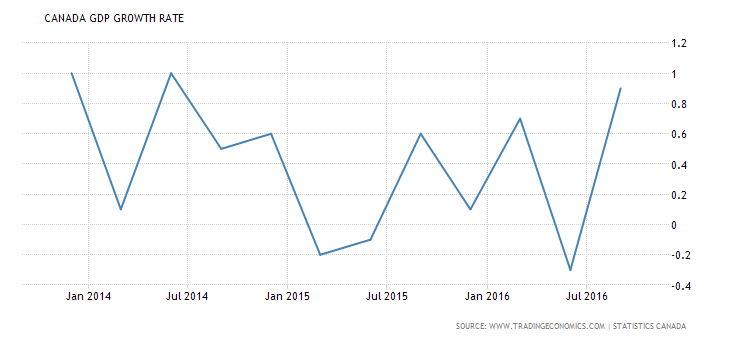
The graph below illustrated Canada’s GDP growth rate over the years:
Social Factors
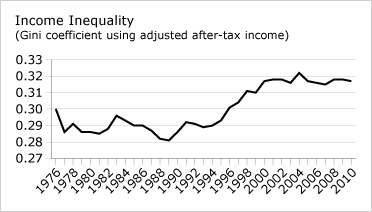
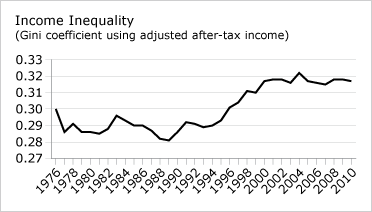
The Median total family income as of 2014 in Canada is $ 78,870. The diagram below illustrates income inequality in Canada, which is numerical displayed via the Gini coefficient;
Source :The conference Board of Canada
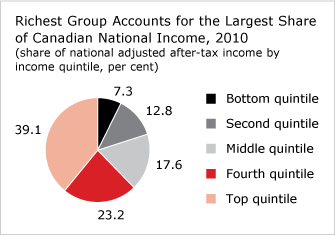
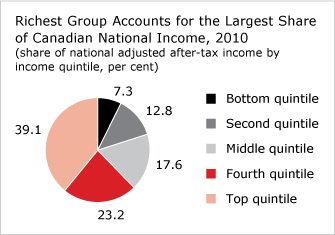
Furthermore, the pie chart below illustrates the manner in which income is shares among socio economic groups I Canada, the bottom quintile refers to those poorest income group, and the top quintile to the richest.
Source :The conference Board of Canada
The International Adult Literacy Survey (IAL), revealed that Canada has a relatively low literacy rate of 40% in the years 2003, when taking into consideration the population between the ages of 16 – 65 yrs. (The conference board of Canada,n.d.)
Technological Factors
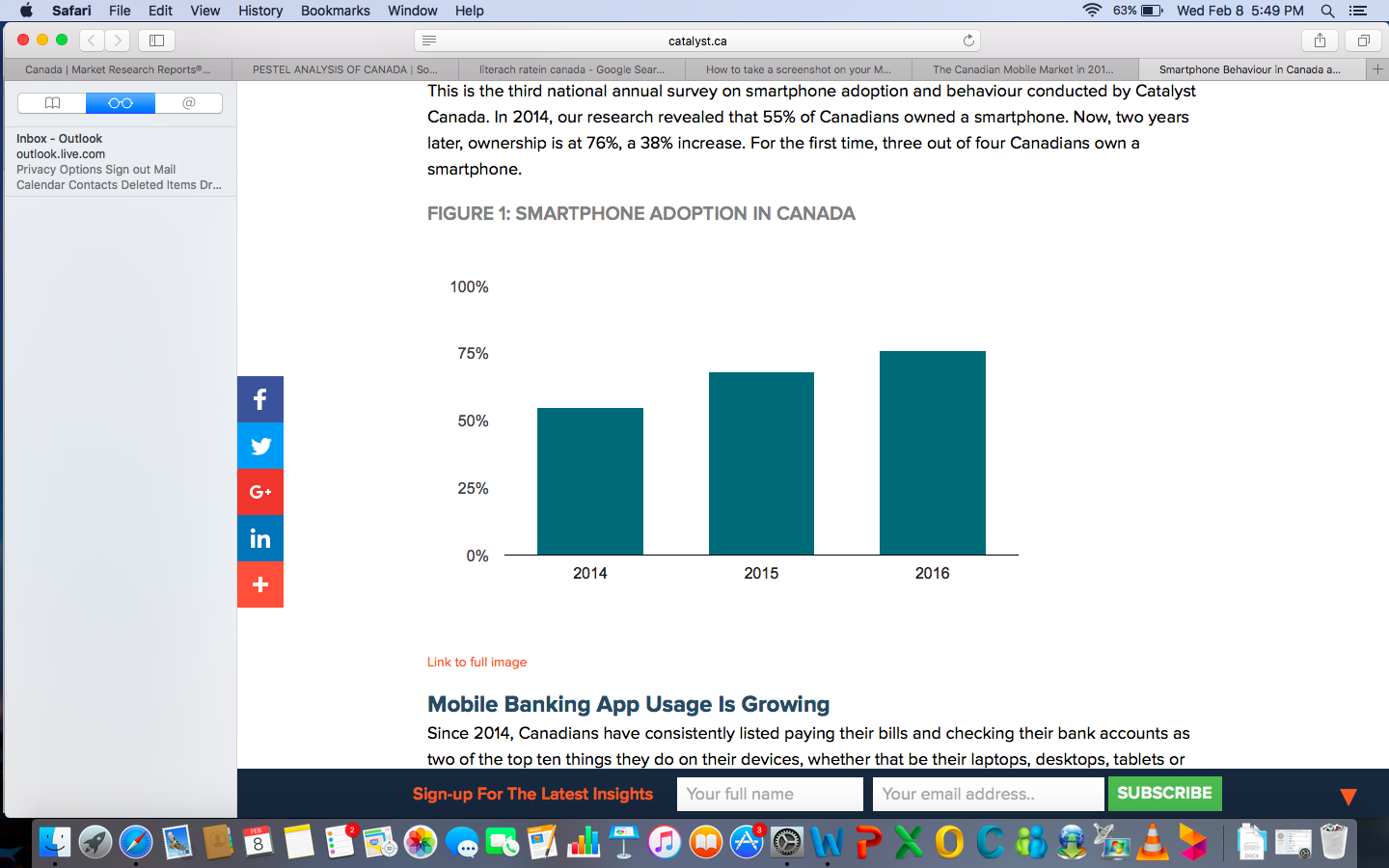
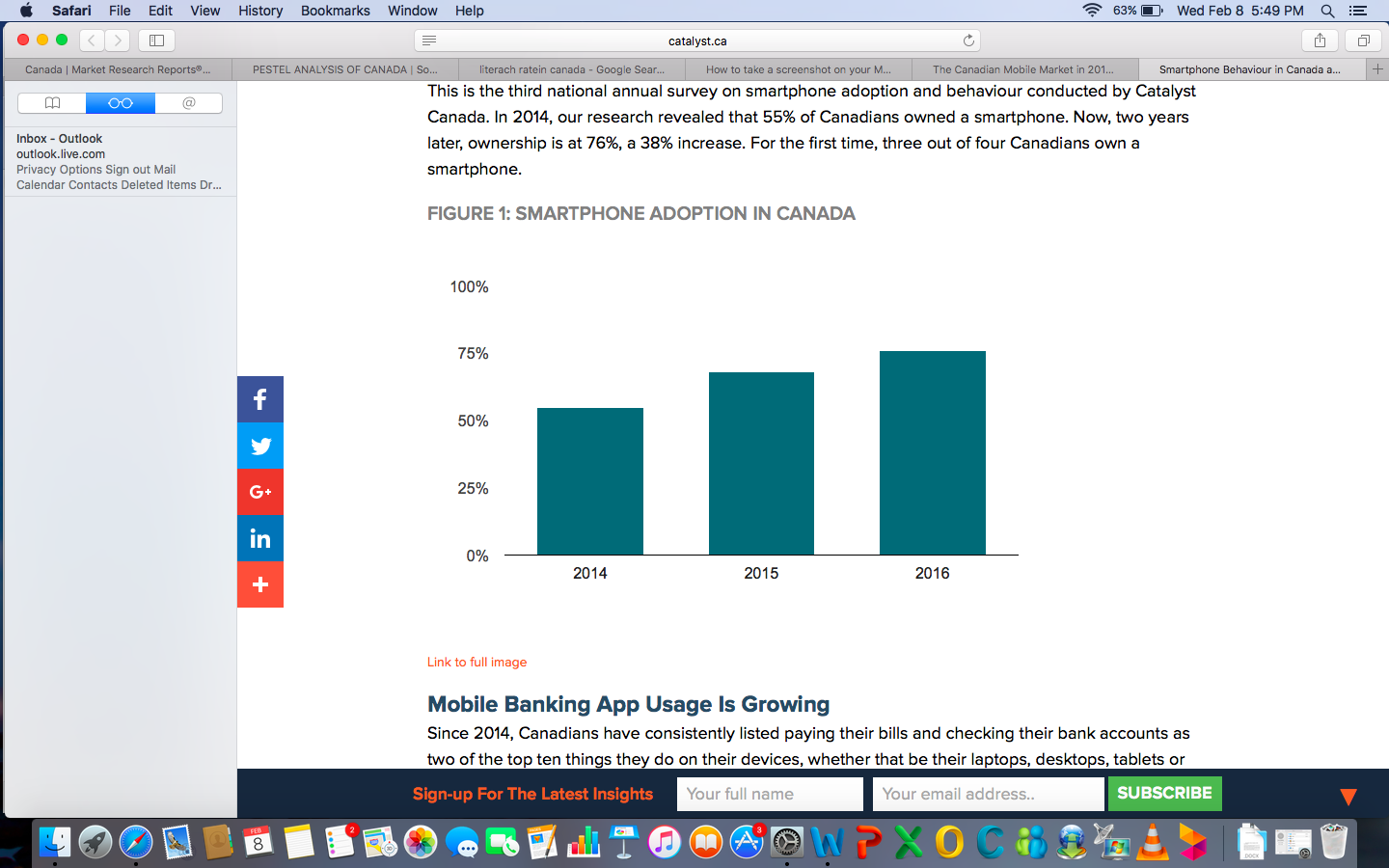
Since the inception of the internet, it has been a key source of information for a majority of Canadians, in fact 85.8% of the population (2013), are internet users. The e- commerce market is flourishing in Canada, in the year 2013 over $136 billion was earned from online sales. Furthermore, mobile phone usage continues to grow in Canada, a study conducted in 2016 revealed that 76% of the population use smart phones. (Frederick , 2016)
China
SWOT Analysis
Strengths
- Abundance of cheap labour.
- Wages in China are merely above the minimum wage level, of approximately $270 a month, which is comparatively cheap to other developed nations. (Jiaxing & Yangon, 2015)
- The rapidly rising population (12-13 million per year), resulting in an escalation in market demand offers an enormous customer base for investors.
- Highly developed infrastructure. In 2016 based on the LPI index, China was ranked 9th in terms of infrastructure. (“Global ranking 2016”, 2016)The Chinese government continues to spend billions of dollars, on mega projects such as the Hinan power grid project, and the Tianhuangping hydroelectric project, to further advance Chinese infrastructure. (Weller, 2017)
- The Chinese government offer attractive incentives for Foreign Direct Investment, such as special economic zones (SEZ), Pudong Zone, Free trade Agreements (FTA’s), Open Costal Areas (OCC’s), and other tax benefits. (Lunes, 2010)
- Rapid economic growth: As of 2015, the Chinese GDP contributes towards17.75% of the world economy; Thus, it can be deemed a lucrative market to invest in.
Weaknesses
- The abundance of counterfeit products being sold in the Chinese market.
- The Chinese economy is heavily dependant on exports, despite its advantages, such dependency resulted in mass production which caused the exploitation of natural resources, and a marked increase in the degree of pollution. (“Chinas strengths and weaknesses”, 2012)
- There is a significant wealth disparity on China, the gini coefficient in 2015 was 0.462 which is reflective of sever income inequality, according to the world bank. (Wildau, 2016)
Opportunities
- Substantial investment in innovation, and research and development. It offers tremendous opportunities for investors. For instance, China is emphasising on the development of renewable alternative forms of energy at a lower cost.
- Immense investment opportunities owing to the countries “long term sustainable economic goals.”
- Substantial infrastructure development facilitates efficient transport, and sale of goods and services. (Perkowski, 2016)
Threats
- Negative global customer perception; owing to the influx of counterfeit products that flood the Chinese market.
- The mounting debt in China, threatens economic progress: China posses a foreign debt of over $1.68 trillion as of 2015. (Fullick, 2016)
- China is facing a number of issues, and accusations regarding heavy pollution and dumping. One primary contributor towards China’s escalating degree of air pollution is it’s heavy reliance on non renewable sources of energy such as coal. (Morales, 2015)
PEST Analysis
Political Factors
The politics of China function as a Socialist Republic, where the Communist party is the sole party in China, which does not tolerate any form of opposition. Over the past decade the Chinese government has payed significant emphasis on the advancement of numerous platforms including e- commerce.
Economic Factors
China posses the worlds second largest economy, when considering its nominal GDP. It has been dubbed the world’s “manufacturing hub, and is termed a market economy according to the WTO. China also posses the worlds third largest bond market, and the government aims to open the latter to foreign investors. (Kavanagh et al, 2016)
Listed below are China’s key economic indicators as of 2017;
GDP (USD,billion) 11008
GDP growth (%) 1.7
GDP per capita(USD) 6498
Unemployment Rate (%) 4.02
Inflation Rate (%) 2.1
Interest Rate (%) 4.35
Source : National Bureau of Statistics China
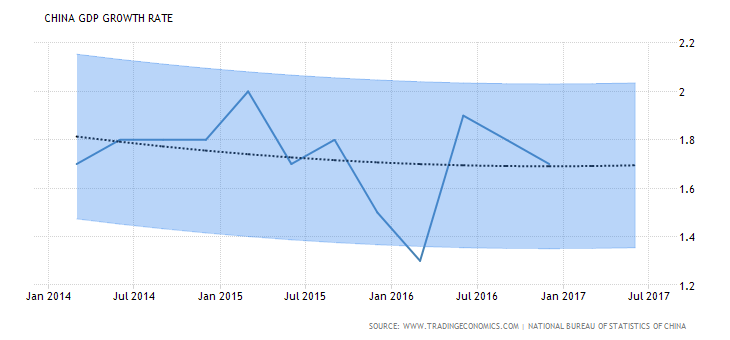
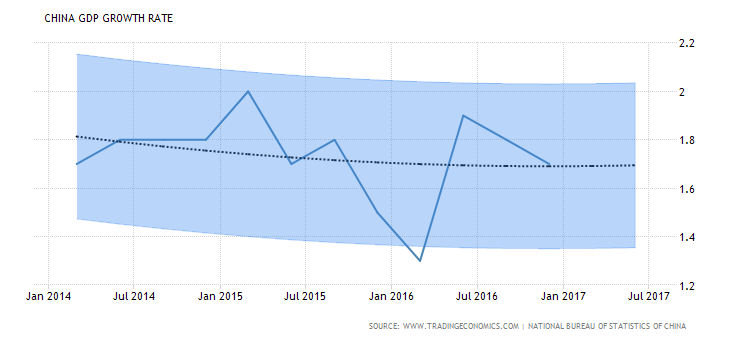
The graph below illustrated China GDP growth rate over the years:
Social Factors
Listed below are Chinas social indicators:
Population (2015) 1375 million
Population growth rate (2013) 0.5%
Unemployment rate (2016) 4.02%
Literacy Rate(2015) 96.4%
Life Expectancy(2012) 75.2 years
Gini coefficient (2015) 46.2
Source : National Bureau of Statistics China
As reflected by the Gini coefficient, the wealth disparity in China is significant. The graph below illustrates the rise of the latter over time, and this signifies higher chances of social unrest.
Technological Factors
China has achieved unprecedented heights in the advancement of science, technology, research and development. In the year 2012 the Chinese government spent over $164 billion on research and development. Furthermore, China has one of the worlds largest Internet population of 667 million, and an internet penetration rate of 48.8%, online shopping rates are sky rocketing, and has one of the worlds largest smart phone user bases of 1.28 billion. (Statistics portal, 2016)
Singapore
SWOT Analysis
Strengths
- Stable political environment, with low threats in terms of terrorism and civil unrest. It has been ranked to be the most politically stable country in Asia. The country also has one of the lowest corruption rate sin the world.
- The country is strategically located in the heart of South East Asia, enabling access to a colossal consumer base.
- The world bank has ranked Singapore as number one, when considering the ease of doing business. The government of Singapore welcomes foreign investors, and provides unpanelled support in setting up.
- Singapore offers very low corporate tax rates (17% per annum), tax reduction schemes and grants, numerous Free Trade Agreements, and offers incentives such as “the double tax treaties” which attract numerous FDI’s.
- Singapore offers flexible immigration policies, and a highly skilled workforce (Kuepper, 2016)
- The country posses the highest income per capita in the world, the highest unemployment rate and the highest concentration of millionaires.
- It has the worlds third largest globalized economy.
- Singapore offers advanced infrastructure, banking and communication facilities in fact, Singapore was ranked as having the worlds second best infrastructure facilities, by the world economic forum. (Holodny,2015)
Weaknesses
- As Singapore is an exportoriented economy, their economic growth is subjected to that of the world. Thus, it is heavily reliant on global demand.
- Purchasing, and renting real estate in Singapore is exorbitantly expensive, owing to the limited land of 710 sq kilo meters available.
- Singapore has a very high labour cost owing to the limited availability of the “low tier” workforce.
Opportunities
- Singapore houses and nurtures numerous emerging markets, which offer substantial benefits to FDI’s.
- Singapore is home to a colossal number of high net worth individuals, which facilitates a higher degree of spending on goods and services.
- E- commerce together with other technological advances are thriving in Singapore, which offer tremendous opportunities for investors.
Threats
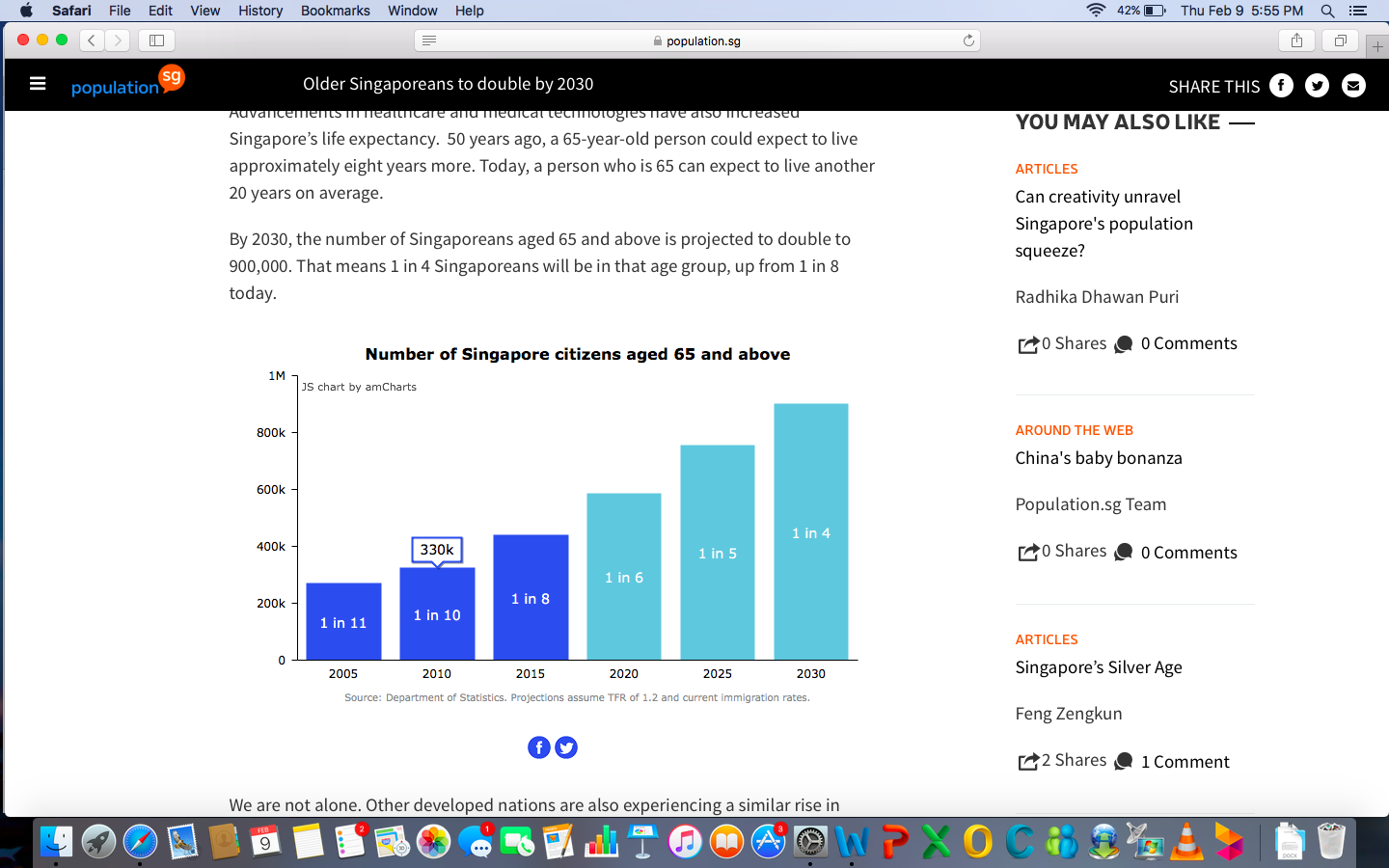
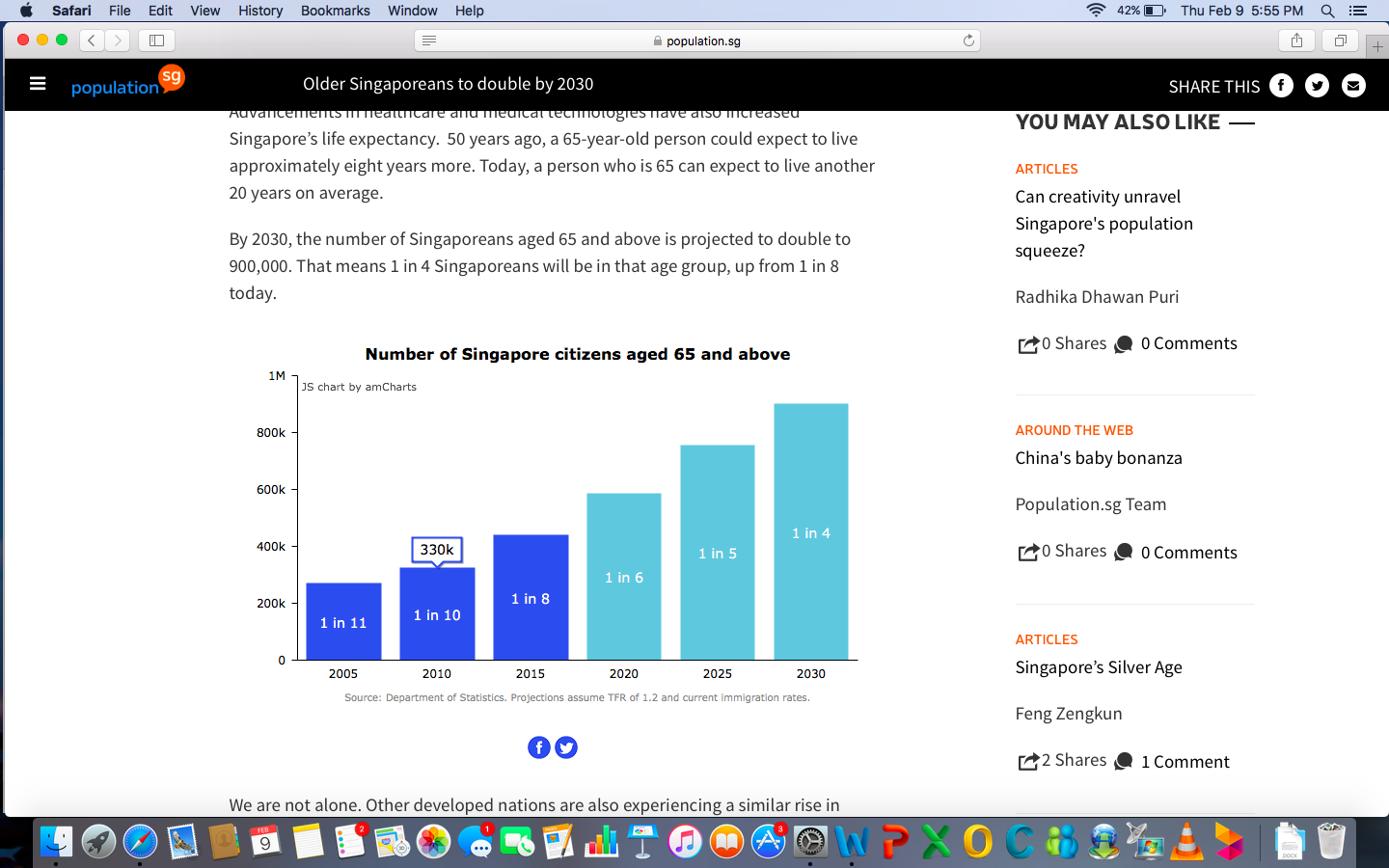
- The rapidly aging population is a significant threat to Singapore. The diagram below illustrates the latter.
- As Singapore is a low lying island, the rising sea level poses an eminent threat.
- Singapore is particularly vulnerable to fluctuations in global food supply and prices, as they import 90% of their food. Thus, natural disasters has a detrimental impact on domestic food supply.
PEST Analysis
Political Factors
Singapore is a parliamentary representative democratic republic. The nation has been rules by the Peoples Action Party since its independence. The World Bank has credited Singapore for having one of the worlds most transparent, and corruption free political system. The political stability of Singapore contributes towards its progress, standard of living and peace.
Economic Factors
Singapore posses a trade oriented market economy. Over the years the Singaporean economy has significantly evolved, today the countries per capita income is the highest in the ASEAN region, it is also the 20th largest export economy in the world, with refined petroleum being the primary contributor.
Listed below are Singapore’s key economic indicators:
GDP (USD, billion) 293
GDP growth (%) 9.1
GDP per capita(USD) 51855
Unemployment Rate (%) 2.2
Inflation Rate (%) 0.2
Interest Rate (%) 0.46
Source : National Bureau of Statistics Singapore
Social Factors
Listed below are Singapore’s social indicators:
Population (2015) 5.54 million
Population growth rate (2013) 1.6 %
Unemployment rate (2016) 2.2%
Literacy Rate(2015) 96.8%
Life Expectancy(2012) 82.14 years
Gini coefficient (2014) 46.4
Source : National Bureau of Statistics Singapore
Singapore has the best quality of living standard in Asia, and its health care is among the best in the world. The country also has a rather diverse population, owing to the influx of foreigners.
Technological Factors
Rapid technological advances have substantially contributed towards Singapore’s success. Statistics suggest that the population in Singapore has stepped into the digital age : Singapore has an online population of 2.9 million, 82% of the internet users also employ social media, 7.3 million mobile subscribers. The previously mentioned figures are astounding; when Singapore has a mere population of 5.54 million. (Wee, 2011)The World Economic Forum has ranked Singapore second in the Global Information Technology report.
2. Selection of the International market using the BERI Index/Matrix
Canada
| Criteria | Weights | Multiplied with the score (rating) on a scale 0-4 | Overall BERI index |
| Political stability | 3 | 3 | 9 |
| Economic growth | 2.5 | 3 | 7.5 |
| Currency convertibility | 2.5 | 3 | 7.5 |
| Labour cost/productivity | 2 | 3 | 6 |
| Short term credit | 2 | 3 | 6 |
| Long term loans/venture capital | 2 | 3 | 6 |
| Attitudes towards foreign investor/profits | 1.5 | 3 | 4.5 |
| Nationalization | 1.5 | 3 | 4.5 |
| Monetary inflation | 1.5 | 2 | 3 |
| Balance of payments | 1.5 | 2 | 3 |
| Enforceability of contracts | 1.5 | 3 | 4.5 |
| Bureaucratic delays | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| Communication: Phone, fax, internet access | 1 | 4 | 4 |
| Local management and partner | 1 | 3 | 3 |
| Professional services and contactors | 0.5 | 3 | 1.5 |
| Total | 25 | 71 |
China
| Criteria | Weights | Multiplied with the score (rating) on a scale 0-4 | Overall BERI index |
| Political stability | 3 | 3 | 9 |
| Economic growth | 2.5 | 4 | 10 |
| Currency convertibility | 2.5 | 3 | 7.5 |
| Labour cost/productivity | 2 | 4 | 8 |
| Short term credit | 2 | 2 | 4 |
| Long term loans/venture capital | 2 | 3 | 6 |
| Attitudes towards foreign investor/profits | 1.5 | 3 | 4.5 |
| Nationalization | 1.5 | 4 | 6 |
| Monetary inflation | 1.5 | 2 | 3 |
| Balance of payments | 1.5 | 2 | 3 |
| Enforceability of contracts | 1.5 | 3 | 4.5 |
| Bureaucratic delays | 1 | 3 | 3 |
| Communication: Phone, fax, internet access | 1 | 3 | 3 |
| Local management and partner | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| Professional services and contactors | 0.5 | 3 | 1.5 |
| Total | 25 | 75 |
Singapore
| Criteria | Weights | Multiplied with the score (rating) on a scale 0-4 | Overall BERI index |
| Political stability | 3 | 4 | 12 |
| Economic growth | 2.5 | 4 | 10 |
| Currency convertibility | 2.5 | 3 | 7.5 |
| Labour cost/productivity | 2 | 3 | 6 |
| Short term credit | 2 | 3 | 6 |
| Long term loans/venture capital | 2 | 3 | 6 |
| Attitudes towards foreign investor/profits | 1.5 | 4 | 6 |
| Nationalization | 1.5 | 2 | 3 |
| Monetary inflation | 1.5 | 2 | 3 |
| Balance of payments | 1.5 | 3 | 4.5 |
| Enforceability of contracts | 1.5 | 4 | 6 |
| Bureaucratic delays | 1 | 3 | 3 |
| Communication: Phone, fax, internet access | 1 | 4 | 4 |
| Local management and partner | 1 | 4 | 4 |
| Professional services and contactors | 0.5 | 3 | 1.5 |
| Total | 25 | 82.5 |
Based on the BERI index of the three countries, it is apparent that Singapore has the most favourable environment for investors.
3. Competitor analysis of the selected market
Based on the analysis I conducted on the internal, and external environment of three potential markets to invest in : Canada, China and Singapore. I believe that Singapore shows the best market potential to invest in.
References
Lane, T. (2014, September 24) Are We There Yet? The United States and Canada after the Global Financial Crisis. Retrieved from http://www.bankofcanada.ca/2014/09/are-we-there-yet/ (February 07, 2017)
CIA. (n.d.) World Fact Book: Canada. Retrieved from https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/ca.html
http://www.focus-economics.com/countries/canada
https://ota.com/sites/default/files/indexed_files/COTA_NationalOrganicMarketSummary.pdf
CIA. (n.d.) World Fact Book: Canada. Retrieved from https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/ca.html
FITT. FITTskills: Global Business Environment, 6th Edition. FITT/Gilmore. VitalBook file.
Foreign Affairs, Trade and Development Canada. (2013) Canada’s State of Trade: Trade and Investment Update 2013. Retrieved from http://www.international.gc.ca/economist-economiste/performance/state-point/state_2013_point/index.aspx?lang=eng#1.0
Lane, T. (2014, September 24) Are We There Yet? The United States and Canada after the Global Financial Crisis. Retrieved from http://www.bankofcanada.ca/2014/09/are-we-there-yet/
McRobie, H. (2009, March 19). Canada’s Banks, the Envy of the World. The Guardian. Retrieved from http://www.theguardian.com/commentisfree/cifamerica/2009/mar/19/canada-us-economy
Smartphone Behaviour in Canada and the Implications for Marketers in 2016
http://www.marketresearchreports.com/countries/canada
https://www.scribd.com/doc/47703002/PESTEL-ANALYSIS-OF-CANADA
http://www.pfsweb.com/blog/2016-canada-ecommerce-market/
http://lpi.worldbank.org/international/global?sort=asc&order=Infrastructure
http://www.pwccn.com/webmedia/doc/634940150734265198_iic_full.pdf
http://gallifordconsulting.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/Doing-Business-in-China-Part-1.pdf
http://moon-mno.blogspot.com/2010/10/government-incentives-fdi-incentives-in.html
http://www.robert-schuman.eu/en/european-issues/0235-china-s-strengths-and-weaknesses
https://www.ft.com/content/3c521faa-baa6-11e5-a7cc-280dfe875e28
http://www.reuters.com/article/us-china-debt-idUSKBN14I0E0
https://ig.ft.com/sites/numbers/economies/china
https://www.statista.com/statistics/278204/china-mobile-users-by-month/
http://www.tradingeconomics.com/china/indicators
https://www.thebalance.com/a-guide-to-investing-in-singapore-1979029
http://www.businessinsider.com.au/wef-countries-best-infrastructure-world-2015-9
Appendix
Appendix A :
ny involves in benchmarking, it can gain competitive advantages. When a company performs benchmarking, it compares it performance with the competitors in the industry and sometimes even with the companies outside the industry with similar practices. There can also be certain situations where the company benchmarks its performance with some of the best units in the organization itself. Through this kind of practices involved in benchmarking, the company is often exposed to identifying either the ways to produce goods or services at a relatively lower price to the competitors or invent new and quality products and thereby to justify a higher price. This is mainly because the company is exposed to the best practices in the industry constantly and is in the process of comparing the company practices and making the corrective actions whenever necessary. Hence it can be concluded
Country Evaluation and Selection
B.Sc.(Hons) in Business & Management
Executive Summary
Table of Contents
Executive Summary 1
Introduction 3
1. External and Internal analysis of the selected three countries. 4
Canada 4
China 8
Singapore 12
References 15
Appendix 17
Appendix A : 18
Introduction
Today, in comparison to conventional foods, the demand for organic food products has drastically escalated, on a global scale. The primary two justifications for the latter, owes to rising consumer awareness on the detrimental impact of consuming toxins, and the contemporary fad of eating healthy.
Thus, for the purpose of this assignment I will take into consideration a hypothetical organization, which is operating in the Organic food Industry. As this paper progresses, I will provide a comprehensive analysis of the potential to expand into overseas markets, as requested by the management of the said hypothetical organization.
1. External and Internal analysis of the selected three countries.
I will analyse the potential of the organic food industry, for the three nations; Canada, Singapore, and China. The analysis will be conducted by comprehensively assessing the internal, and external environment by employing two analytical tools; PEST, and SWOT analysis.
Canada
SWOT Analysis
Strengths
- Strong fiscal policies, and robust financial sector. The latter is the key justification as to why Canada was capable of recovering from the 2008 recession, relatively quickly in comparison to other nations. (Lane, 2014)
- The Canadian banks are ranked among the best in the world according to the World Economic Forum.
- Canada has substantially benefitted from the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), enabling the country to enjoy a considerable trade surplus. (“The World Factbook: Canada ”, 2017)
- Significant entrepreneurial support offered by the Canadian government, enabling one to benefit from tax reductions, and breaks.
Weaknesses
- Canada’s substantial dependency on the United States as a “trading partner”. A considerable sum (74.5%), of the nations exports is sent to the United States, whereas the United States imports a mere 14.1 % from Canada. Thus, this dependency had a significant toll on Canadian export market following the recession. (Lane, 2014)
Opportunities
- The Canadian market offers tremendous opportunities, particularly in the organic food market. In comparison to other agro foods, the Canadian organic food market has tripled since 2006, and is valued at over“ $ 3.5 bn per year in sales.” (Mackinnon, 2013)
- increasing government regulations on Agro foods, the promotion of organic food, and increasing consumer awareness on the benefits of consuming the latter provides tremendous opportunity for new investors in this sector.
Threats
- The EU debt crisis serves a potential threat to the Canadian economy.
- The FTA between Canada and Europe can be detrimental to Canada owing to the economic stagnation of Europe.
- New entrants will face a substantial threat from existing local firms, “The organic market in Canada has also grown exponentially over a very short period, to the point that it is now the fourth largest in the world.” (Mackinnon, 2013)
PEST Analysis
Political Factors
The Canadian government is a democracy, consisting of a “parliamentary government.” Canada can be credited for engaging in numerous free trade agreements, which will contribute towards the enhancement of its economy, “facilitate bilateral free trade, avoid double taxation, protect foreign investment, strengthen financial and banking institutions, and assist development.” (“Canada”, n.d.)
Economical Factors
Not only is Canada among the worlds wealthiest nations, the Canadian economy can also be credited for being among the world’s best performing. It has the world’s 10th largest economy in terms of nominal GDP, and 15th largest in terms of Purchasing Power Parity. Furthermore, it is also among the group of G-7 nations. (“Canada Economic Forecast”, 2017)
Illustrated below are Canada’s key economic indicator as of 2017;
GDP (USD,billion) 1551
GDP growth (%) 0.9
GDP per capita(USD) 50001
Unemployment Rate (%) 6.09
Inflation Rate (%) 1.5
Interest Rate (%) 0.5
Source : National Bureau of Statistics Canada
The graph below illustrated Canada’s GDP growth rate over the years:
Social Factors
The Median total family income as of 2014 in Canada is $ 78,870. The diagram below illustrates income inequality in Canada, which is numerical displayed via the Gini coefficient;
Source :The conference Board of Canada
Furthermore, the pie chart below illustrates the manner in which income is shares among socio economic groups I Canada, the bottom quintile refers to those poorest income group, and the top quintile to the richest.
Source :The conference Board of Canada
The International Adult Literacy Survey (IAL), revealed that Canada has a relatively low literacy rate of 40% in the years 2003, when taking into consideration the population between the ages of 16 – 65 yrs. (The conference board of Canada,n.d.)
Technological Factors
Since the inception of the internet, it has been a key source of information for a majority of Canadians, in fact 85.8% of the population (2013), are internet users. The e- commerce market is flourishing in Canada, in the year 2013 over $136 billion was earned from online sales. Furthermore, mobile phone usage continues to grow in Canada, a study conducted in 2016 revealed that 76% of the population use smart phones. (Frederick , 2016)
China
SWOT Analysis
Strengths
- Abundance of cheap labour.
- Wages in China are merely above the minimum wage level, of approximately $270 a month, which is comparatively cheap to other developed nations. (Jiaxing & Yangon, 2015)
- The rapidly rising population (12-13 million per year), resulting in an escalation in market demand offers an enormous customer base for investors.
- Highly developed infrastructure. In 2016 based on the LPI index, China was ranked 9th in terms of infrastructure. (“Global ranking 2016”, 2016)The Chinese government continues to spend billions of dollars, on mega projects such as the Hinan power grid project, and the Tianhuangping hydroelectric project, to further advance Chinese infrastructure. (Weller, 2017)
- The Chinese government offer attractive incentives for Foreign Direct Investment, such as special economic zones (SEZ), Pudong Zone, Free trade Agreements (FTA’s), Open Costal Areas (OCC’s), and other tax benefits. (Lunes, 2010)
- Rapid economic growth: As of 2015, the Chinese GDP contributes towards17.75% of the world economy; Thus, it can be deemed a lucrative market to invest in.
Weaknesses
- The abundance of counterfeit products being sold in the Chinese market.
- The Chinese economy is heavily dependant on exports, despite its advantages, such dependency resulted in mass production which caused the exploitation of natural resources, and a marked increase in the degree of pollution. (“Chinas strengths and weaknesses”, 2012)
- There is a significant wealth disparity on China, the gini coefficient in 2015 was 0.462 which is reflective of sever income inequality, according to the world bank. (Wildau, 2016)
Opportunities
- Substantial investment in innovation, and research and development. It offers tremendous opportunities for investors. For instance, China is emphasising on the development of renewable alternative forms of energy at a lower cost.
- Immense investment opportunities owing to the countries “long term sustainable economic goals.”
- Substantial infrastructure development facilitates efficient transport, and sale of goods and services. (Perkowski, 2016)
Threats
- Negative global customer perception; owing to the influx of counterfeit products that flood the Chinese market.
- The mounting debt in China, threatens economic progress: China posses a foreign debt of over $1.68 trillion as of 2015. (Fullick, 2016)
- China is facing a number of issues, and accusations regarding heavy pollution and dumping. One primary contributor towards China’s escalating degree of air pollution is it’s heavy reliance on non renewable sources of energy such as coal. (Morales, 2015)
PEST Analysis
Political Factors
The politics of China function as a Socialist Republic, where the Communist party is the sole party in China, which does not tolerate any form of opposition. Over the past decade the Chinese government has payed significant emphasis on the advancement of numerous platforms including e- commerce.
Economic Factors
China posses the worlds second largest economy, when considering its nominal GDP. It has been dubbed the world’s “manufacturing hub, and is termed a market economy according to the WTO. China also posses the worlds third largest bond market, and the government aims to open the latter to foreign investors. (Kavanagh et al, 2016)
Listed below are China’s key economic indicators as of 2017;
GDP (USD,billion) 11008
GDP growth (%) 1.7
GDP per capita(USD) 6498
Unemployment Rate (%) 4.02
Inflation Rate (%) 2.1
Interest Rate (%) 4.35
Source : National Bureau of Statistics China
The graph below illustrated China GDP growth rate over the years:
Social Factors
Listed below are Chinas social indicators:
Population (2015) 1375 million
Population growth rate (2013) 0.5%
Unemployment rate (2016) 4.02%
Literacy Rate(2015) 96.4%
Life Expectancy(2012) 75.2 years
Gini coefficient (2015) 46.2
Source : National Bureau of Statistics China
As reflected by the Gini coefficient, the wealth disparity in China is significant. The graph below illustrates the rise of the latter over time, and this signifies higher chances of social unrest.
Technological Factors
China has achieved unprecedented heights in the advancement of science, technology, research and development. In the year 2012 the Chinese government spent over $164 billion on research and development. Furthermore, China has one of the worlds largest Internet population of 667 million, and an internet penetration rate of 48.8%, online shopping rates are sky rocketing, and has one of the worlds largest smart phone user bases of 1.28 billion. (Statistics portal, 2016)
Singapore
SWOT Analysis
Strengths
- Stable political environment, with low threats in terms of terrorism and civil unrest. It has been ranked to be the most politically stable country in Asia. The country also has one of the lowest corruption rate sin the world.
- The country is strategically located in the heart of South East Asia, enabling access to a colossal consumer base.
- The world bank has ranked Singapore as number one, when considering the ease of doing business. The government of Singapore welcomes foreign investors, and provides unpanelled support in setting up.
- Singapore offers very low corporate tax rates (17% per annum), tax reduction schemes and grants, numerous Free Trade Agreements, and offers incentives such as “the double tax treaties” which attract numerous FDI’s.
- Singapore offers flexible immigration policies, and a highly skilled workforce (Kuepper, 2016)
- The country posses the highest income per capita in the world, the highest unemployment rate and the highest concentration of millionaires.
- It has the worlds third largest globalized economy.
- Singapore offers advanced infrastructure, banking and communication facilities in fact, Singapore was ranked as having the worlds second best infrastructure facilities, by the world economic forum. (Holodny,2015)
Weaknesses
- As Singapore is an exportoriented economy, their economic growth is subjected to that of the world. Thus, it is heavily reliant on global demand.
- Purchasing, and renting real estate in Singapore is exorbitantly expensive, owing to the limited land of 710 sq kilo meters available.
- Singapore has a very high labour cost owing to the limited availability of the “low tier” workforce.
Opportunities
- Singapore houses and nurtures numerous emerging markets, which offer substantial benefits to FDI’s.
- Singapore is home to a colossal number of high net worth individuals, which facilitates a higher degree of spending on goods and services.
- E- commerce together with other technological advances are thriving in Singapore, which offer tremendous opportunities for investors.
Threats
- The rapidly aging population is a significant threat to Singapore. The diagram below illustrates the latter.
- As Singapore is a low lying island, the rising sea level poses an eminent threat.
- Singapore is particularly vulnerable to fluctuations in global food supply and prices, as they import 90% of their food. Thus, natural disasters has a detrimental impact on domestic food supply.
PEST Analysis
Political Factors
Singapore is a parliamentary representative democratic republic. The nation has been rules by the Peoples Action Party since its independence. The World Bank has credited Singapore for having one of the worlds most transparent, and corruption free political system. The political stability of Singapore contributes towards its progress, standard of living and peace.
Economic Factors
Singapore posses a trade oriented market economy. Over the years the Singaporean economy has significantly evolved, today the countries per capita income is the highest in the ASEAN region, it is also the 20th largest export economy in the world, with refined petroleum being the primary contributor.
Listed below are Singapore’s key economic indicators:
GDP (USD, billion) 293
GDP growth (%) 9.1
GDP per capita(USD) 51855
Unemployment Rate (%) 2.2
Inflation Rate (%) 0.2
Interest Rate (%) 0.46
Source : National Bureau of Statistics Singapore
Social Factors
Listed below are Singapore’s social indicators:
Population (2015) 5.54 million
Population growth rate (2013) 1.6 %
Unemployment rate (2016) 2.2%
Literacy Rate(2015) 96.8%
Life Expectancy(2012) 82.14 years
Gini coefficient (2014) 46.4
Source : National Bureau of Statistics Singapore
Singapore has the best quality of living standard in Asia, and its health care is among the best in the world. The country also has a rather diverse population, owing to the influx of foreigners.
Technological Factors
Rapid technological advances have substantially contributed towards Singapore’s success. Statistics suggest that the population in Singapore has stepped into the digital age : Singapore has an online population of 2.9 million, 82% of the internet users also employ social media, 7.3 million mobile subscribers. The previously mentioned figures are astounding; when Singapore has a mere population of 5.54 million. (Wee, 2011)The World Economic Forum has ranked Singapore second in the Global Information Technology report.
2. Selection of the International market using the BERI Index/Matrix
Canada
| Criteria | Weights | Multiplied with the score (rating) on a scale 0-4 | Overall BERI index |
| Political stability | 3 | 3 | 9 |
| Economic growth | 2.5 | 3 | 7.5 |
| Currency convertibility | 2.5 | 3 | 7.5 |
| Labour cost/productivity | 2 | 3 | 6 |
| Short term credit | 2 | 3 | 6 |
| Long term loans/venture capital | 2 | 3 | 6 |
| Attitudes towards foreign investor/profits | 1.5 | 3 | 4.5 |
| Nationalization | 1.5 | 3 | 4.5 |
| Monetary inflation | 1.5 | 2 | 3 |
| Balance of payments | 1.5 | 2 | 3 |
| Enforceability of contracts | 1.5 | 3 | 4.5 |
| Bureaucratic delays | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| Communication: Phone, fax, internet access | 1 | 4 | 4 |
| Local management and partner | 1 | 3 | 3 |
| Professional services and contactors | 0.5 | 3 | 1.5 |
| Total | 25 | 71 |
China
| Criteria | Weights | Multiplied with the score (rating) on a scale 0-4 | Overall BERI index |
| Political stability | 3 | 3 | 9 |
| Economic growth | 2.5 | 4 | 10 |
| Currency convertibility | 2.5 | 3 | 7.5 |
| Labour cost/productivity | 2 | 4 | 8 |
| Short term credit | 2 | 2 | 4 |
| Long term loans/venture capital | 2 | 3 | 6 |
| Attitudes towards foreign investor/profits | 1.5 | 3 | 4.5 |
| Nationalization | 1.5 | 4 | 6 |
| Monetary inflation | 1.5 | 2 | 3 |
| Balance of payments | 1.5 | 2 | 3 |
| Enforceability of contracts | 1.5 | 3 | 4.5 |
| Bureaucratic delays | 1 | 3 | 3 |
| Communication: Phone, fax, internet access | 1 | 3 | 3 |
| Local management and partner | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| Professional services and contactors | 0.5 | 3 | 1.5 |
| Total | 25 | 75 |
Singapore
| Criteria | Weights | Multiplied with the score (rating) on a scale 0-4 | Overall BERI index |
| Political stability | 3 | 4 | 12 |
| Economic growth | 2.5 | 4 | 10 |
| Currency convertibility | 2.5 | 3 | 7.5 |
| Labour cost/productivity | 2 | 3 | 6 |
| Short term credit | 2 | 3 | 6 |
| Long term loans/venture capital | 2 | 3 | 6 |
| Attitudes towards foreign investor/profits | 1.5 | 4 | 6 |
| Nationalization | 1.5 | 2 | 3 |
| Monetary inflation | 1.5 | 2 | 3 |
| Balance of payments | 1.5 | 3 | 4.5 |
| Enforceability of contracts | 1.5 | 4 | 6 |
| Bureaucratic delays | 1 | 3 | 3 |
| Communication: Phone, fax, internet access | 1 | 4 | 4 |
| Local management and partner | 1 | 4 | 4 |
| Professional services and contactors | 0.5 | 3 | 1.5 |
| Total | 25 | 82.5 |
Based on the BERI index of the three countries, it is apparent that Singapore has the most favourable environment for investors.
3. Competitor analysis of the selected market
Based on the analysis I conducted on the internal, and external environment of three potential markets to invest in : Canada, China and Singapore. I believe that Singapore shows the best market potential to invest in.
References
Lane, T. (2014, September 24) Are We There Yet? The United States and Canada after the Global Financial Crisis. Retrieved from http://www.bankofcanada.ca/2014/09/are-we-there-yet/ (February 07, 2017)
CIA. (n.d.) World Fact Book: Canada. Retrieved from https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/ca.html
http://www.focus-economics.com/countries/canada
https://ota.com/sites/default/files/indexed_files/COTA_NationalOrganicMarketSummary.pdf
CIA. (n.d.) World Fact Book: Canada. Retrieved from https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/ca.html
FITT. FITTskills: Global Business Environment, 6th Edition. FITT/Gilmore. VitalBook file.
Foreign Affairs, Trade and Development Canada. (2013) Canada’s State of Trade: Trade and Investment Update 2013. Retrieved from http://www.international.gc.ca/economist-economiste/performance/state-point/state_2013_point/index.aspx?lang=eng#1.0
Lane, T. (2014, September 24) Are We There Yet? The United States and Canada after the Global Financial Crisis. Retrieved from http://www.bankofcanada.ca/2014/09/are-we-there-yet/
McRobie, H. (2009, March 19). Canada’s Banks, the Envy of the World. The Guardian. Retrieved from http://www.theguardian.com/commentisfree/cifamerica/2009/mar/19/canada-us-economy
Smartphone Behaviour in Canada and the Implications for Marketers in 2016
http://www.marketresearchreports.com/countries/canada
https://www.scribd.com/doc/47703002/PESTEL-ANALYSIS-OF-CANADA
http://www.pfsweb.com/blog/2016-canada-ecommerce-market/
http://lpi.worldbank.org/international/global?sort=asc&order=Infrastructure
http://www.pwccn.com/webmedia/doc/634940150734265198_iic_full.pdf
http://gallifordconsulting.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/Doing-Business-in-China-Part-1.pdf
http://moon-mno.blogspot.com/2010/10/government-incentives-fdi-incentives-in.html
http://www.robert-schuman.eu/en/european-issues/0235-china-s-strengths-and-weaknesses
https://www.ft.com/content/3c521faa-baa6-11e5-a7cc-280dfe875e28
http://www.reuters.com/article/us-china-debt-idUSKBN14I0E0
https://ig.ft.com/sites/numbers/economies/china
https://www.statista.com/statistics/278204/china-mobile-users-by-month/
http://www.tradingeconomics.com/china/indicators
https://www.thebalance.com/a-guide-to-investing-in-singapore-1979029
http://www.businessinsider.com.au/wef-countries-best-infrastructure-world-2015-9


13 comments